LIGO scientists receive 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2017 was awarded by The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to the principal scientists working on LIGO, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory. One half of the award goes to Rainer Weiss and the other half jointly to Barry C. Barish and Kip S. Thorne, all with the LIGO/VIRGO Collaboration, "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
RELATED ARTICLE: LIGO detects gravitational waves again!
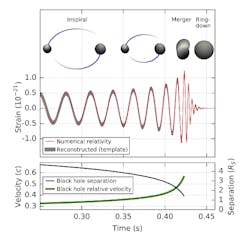
On 14 September 2015, the universe's gravitational waves were observed for the very first time. The waves, which were predicted by Albert Einstein a hundred years ago, came from a collision between two black holes. It took 1.3 billion years for the waves to arrive at the LIGO detector in the USA. The signal was extremely weak when it reached Earth, but is already promising a revolution in astrophysics. Gravitational waves are an entirely new way of observing the most violent events in space and testing the limits of our knowledge.
LIGO is a collaborative project with more than 1000 researchers from more than 20 countries. Together, they have realized a vision that is almost fifty years old. The 2017 Nobel Laureates have, with their enthusiasm and determination, each been invaluable to the success of LIGO. Pioneers Rainer Weiss and Kip S. Thorne, together with Barry C. Barish, the scientist and leader who brought the project to completion, ensured that four decades of effort led to gravitational waves finally being observed.
In the mid-1970s, Rainer Weiss had already analyzed possible sources of background noise that would disturb measurements, and had also designed a detector, a laser-based interferometer, that would overcome this noise. Early on, both Kip Thorne and Rainer Weiss were firmly convinced that gravitational waves could be detected and bring about a revolution in our knowledge of the universe.
Gravitational waves spread at the speed of light, filling the universe, as Albert Einstein described in his general theory of relativity. They are always created when a mass accelerates, like when an ice-skater pirouettes or a pair of black holes rotate around each other. Einstein was convinced it would never be possible to measure them. The LIGO project's achievement was using a pair of gigantic laser interferometers to measure a change thousands of times smaller than an atomic nucleus, as the gravitational wave passed the Earth.
So far all sorts of electromagnetic radiation and particles, such as cosmic rays or neutrinos, have been used to explore the universe. However, gravitational waves are direct testimony to disruptions in spacetime itself. This is something completely new and different, opening up unseen worlds. A wealth of discoveries awaits those who succeed in capturing the waves and interpreting their message.
SOURCE: Nobelprize.org (official website of the Nobel Prize); https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/2017/press.html

Gail Overton | Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.