SCOT S. OLIVIER, STEVEN M. JONES, DIANA C. CHEN, ROBERT J. ZAWADZKI, STACEY S. CHOI, SOPHIE P. LAUT, and JOHN S. WERNER
Optical-coherence tomography (OCT) has recently gained widespread popularity among ophthalmologists for use in the clinical diagnosis and monitoring of human retinal disease. The key to this success is the ability of OCT to make noninvasive, in vivo measurements of the thickness of specific retinal layers—such as the nerve-fiber layer, which thins in patients with glaucoma. Current commercial OCT instruments use a “time-domain” approach in which coherent interference between light from the retina and a uniform reference sample is used to measure the reflectance of retinal tissue in a series of axial depth locations—called an “A-scan.” Multiple A-scans are then obtained at a sequence of lateral locations, called a “B-scan,” to produce a 2-D image “slice” of the retina. These image slices can be collected at multiple locations throughout a subject’s eye to provide an assessment of the overall health of retinal structures.
Fourier-domain OCT
A new method called Fourier-domain OCT (FD-OCT) has recently demonstrated performance enhancements compared to the time-domain OCT imaging technique. Fourier-domain OCT offers a significant advantage in sensitivity and acquisition speed.1 Its differentiating feature is that data on the reflectance of the retinal tissue at each axial depth location is obtained simultaneously by recording the wavelength spectrum of the coherent interference between light reflected from the retina and the reference sample. This spectrum contains information about the reflectivity at each axial depth, which can be recovered by computing the inverse Fourier transform of the spectrum. Although the FD-OCT is an advance over the standard time-domain approach, the ability to visualize clinically important structures in the eye is still limited in both methods by their image resolution.
The resolution of OCT systems in the axial dimension is set by the coherence properties of the light source. Current light sources can provide axial resolution below 3 µm, which is more than sufficient to resolve the axial dimensions of most retinal cells.2 The lateral resolution is set by the diffraction limit of the pupil of the subject’s eye. For most subjects, the pupil can be dilated to at least 6 mm using standard pharmaceuticals, giving a diffraction-limited resolution of less than 3 µm. In practice, however, the lateral resolution is substantially degraded from the diffraction limit by optical aberrations present in the eye. Consequently, most ophthalmic OCT systems are designed to be operated with a lateral resolution in the range of 15 to 20 µm, which is insufficient to allow visualization of many clinically important retinal cells such as cone photoreceptors, which are damaged in many retinal diseases, including diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration, two leading causes of blindness in developed countries.
OCT using adaptive optics
The solution for improving lateral resolution in ophthalmic OCT imaging is the use of adaptive optics (AO) to correct for the aberrations in the eye. Adaptive optics work by measuring aberrations using a wavefront sensor (for example, a Shack-Hartmann sensor) and applying this information to the control of a deformable mirror in a closed loop, thereby compensating for the measured aberrations. This approach to improving the lateral resolution has previously been demonstrated in other retinal-imaging modalities, first in digital fundus cameras and more recently in scanning laser ophthalmoscopes.3, 4 For these instruments, the use of AO has been shown to produce retinal imagery at or near the diffraction limit.
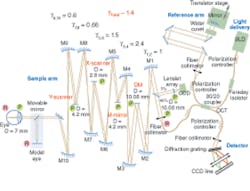
Capitalizing on the demonstrated success of AO to correct ocular aberrations, several groups have recently combined AO with OCT, seeking to produce the first capability for noninvasive, in vivo, 3‑D visualization of the human retina at the cellular level.5 Researchers at the University of California (UC) Davis Medical Center and the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have collaborated to develop one of these systems (see Fig. 1).
This instrument successfully combines the advantages of FD-OCT and advanced microtechnology for adaptive optics, using a 35-element bimorph deformable mirror (DM) built by AOptix Technologies (Campbell, CA) that was originally developed for use in wireless laser communications. Use of this bimorph DM, which has a large range of surface deformation (up to ±16 µm) enables correction of up to ±3 diopters of defocus and enables the focal plane of the instrument, which has a depth of focus of about 60 µm, to be scanned axially through the retina to optimize the visualization of specific layers.
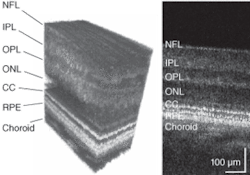
The AO system for the UC Davis/LLNL instrument measures the aberrations in the subject’s eye using a fraction of the OCT imaging light reflected from the retina, which is directed into a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. This information is used to control the bimorph DM, thereby compensating for the measured aberrations. In one experimental example, the reconstructed rms (root-mean-square) wavefront error was measured in a test subject before and during AO correction, together with the Zernike decompositions of the measured aberrations (see Fig. 2). Results show that the AO system can effectively compensate low-order aberrations and maintain low rms wavefront error during closed-loop operation.To evaluate the structures in different retinal layers, an average 1-D power spectrum was calculated for the 200 B-scans in the 3-D volume images. A clear peak in the power spectrum was seen in the photoreceptor layer at the connecting cilia, due to regular structures (see Fig. 3, B-scan). The observed peaks in the spatial frequency correlate with cone-to-cone spacing observed in AO flood-illumination systems as well as that reported for cone-photoreceptor mosaics studied by histology, conclusively demonstrating that the structures seen in the images in this layer are resolved photoreceptors.
Future work will include the use of an additional DM to better correct the higher-order aberrations and the development of image-processing and real-time retinal-tracking techniques to reduce artifacts due to eye motion. A detailed comparison of imagery obtained from AO FD-OCT, scanning-laser ophthalmoscopes and digital fundus photography using AO is also planned. But the preliminary results from AO-OCT systems are already demonstrating the promise of this ophthalmic-imaging modality for providing a new, clinically important view into the human eye.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge OCT assistance from J.A. Izatt, M. Zhao, and B.A. Bower at Duke University. Alfred R. Fuller, David F. Wiley, and Bernd Hamann from the UC Davis Institute of Data Analysis and Visualization developed the 3-D visualization software. Donald T. Miller, Ravi Jonnal, Jungtea Rha, and Yan Zhang, the School of Optometry, Indiana University, Bloomington, contributed to the work on combining AO and OCT. David A. Horsley from the UC Davis Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering Dept. assisted in the testing of the bimorph deformable mirror. This research was supported by the National Eye Institute (grant EY 014743). Additional support was provided by the Dept. of Energy Biomedical Engineering Program. Portions were performed under the auspices of the U.S. Dept. of Energy by University of California Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory contract No. W-7405-Eng-48.
REFERENCES
1. M. Wojtkowski et al., J. Biomed. Opt. 7, 457 (2002).
2. W. Drexler et al., Nature Med. 7, 502 (2000).
3. J. Liang et al., J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 14, 2884 (1997).
4. A. Roorda et al., Optics Express 10, 405 (2002).
5. R.J. Zawadzki et al., Optics Exp. 13, 8532 (2005).
Scot S. Olivier, Steven M. Jones, and Diana C. Chen are at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 7000 East Avenue, L-210, Livermore, California 94550; e-mail: [email protected]. Robert J. Zawadzki, Stacey S. Choi, Sophie P. Laut, and John S. Werner are at the Department of Ophthalmology and Vision Science, UC Davis, 4860 Y Street, Suite 2400, Sacramento, CA 95817.