Evanescent polarization-induced technique enables nanometer-scale imaging
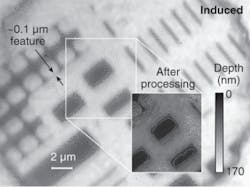
Using a solid-immersion lens (SIL), which does not affect or contaminate the sample like liquid-immersion systems and also enables imaging at numerical-aperture (NA) values greater than 2, researchers in the College of Optical Sciences at theUniversity of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) have demonstrated an induced-polarization evanescent-imaging technique that achieves nanometer-scale vertical resolution and high lateral resolution over a relatively large field of view.
The flat side of the hemispherical SIL is placed just above the sample to be measured. The small gap height (less than the wavelength of the imaging light) enables contrast-enhanced evanescent coupling of the light between the SIL and the sample, inducing a polarization state at the pupil of the objective lens. This information is then imaged onto a CCD and analyzed using a vector plane-wave decomposition model to determine the physical dimensions of the sample under test. Experiments using a patterned silicon wafer and a known reference target with NA of 1.5 confirm a lateral resolution of approximately 175 nm (better than a conventional far-field microscope without scanning or immersion oil) and a height accuracy of ±2 nm in a 25 µm field of view. Contact Tom Milster at [email protected].