Cylindrical luminescent solar concentrators are more efficient if they're hollow
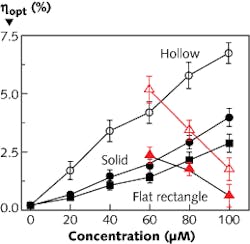
Luminescent solar concentrators in the form of hollow cylinders have higher absorption of solar radiation and lower self-absorption than those shaped as planes or solid cylinders, say scientists at the University of California–Merced. In a luminescent solar concentrator, solar radiation is absorbed by a fluorescent material in an otherwise transparent material; the material downconverts the light, emitting it so the light (mostly) totally internally reflects and is concentrated and collected by solar cells. Self-absorption (reabsorption of the downconverted light before it reaches the solar cells) is one of the main obstacles to wider use of this type of solar concentrator, another being degradation of the downconversion material.
The researchers used near-infrared lead sulfide quantum dots (QDs) as the downconverter and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) as the host. They fabricated examples of the three geometries using QD concentrations from zero to 100 micromolar (μM), with optical efficiencies scaling approximately linearly with QD concentration for all geometries, and peaking at about 7%, 4%, and 3% respectively for the hollow cylinder, solid cylinder, and flat rectangle all at a 100 μM QD concentration (black data points). However, at QD concentrations greater than 60 μM, the output showed degradation when retested after six months (red data points), possibly as a result of interdot energy-transfer events causing a net increase in overall luminescence quenching. Other types of QDs could boost the efficiency by several times. Contact Sayantani Ghosh at [email protected].
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.
