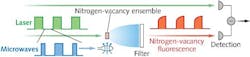
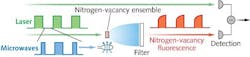
Multiple diamond defects provide subpicotesla magnetometer sensitivity
A single nitrogen-vacancy defect center in a diamond can, when its optical properties and spin properties are queried by laser readout (for example, measuring the resulting polarization), serve as a magnetometer with a room-temperature sensitivity of around 10 nT/Hz0.5. Researchers at the University of Stuttgart (Germany) and the University of Tsukuba (Japan) have demonstrated that this limited sensitivity can be boosted by using multiple defect centers simultaneously to measure magnetic field; in fact, the sensitivity scales as N0.5, where N is the number of defects. To do this, they reduced noise from the green excitation and readout laser and other sources, achieving a room-temperature magnetic-field sensitivity of 0.9 pT/Hz0.5, an improvement of three orders of magnitude over previous results. The detector volume of 8.5 x 10-4 mm3 contained about 1.4 x 1011 nitrogen-vacancy defect centers.
In the setup, a parabolically shaped glass lens contacting the diamond collected the fluorescence photons, directing them to a single photodetector. Software simulations of the arrangement showed a collection efficiency >60%. A laser power of 400 mW focused to a 47-μm-diameter spot provides the excitation and readout light. To make a measurement, the nitrogen-vacancy spins are first polarized with a laser pulse; microwaves then prepare the centers for readout. A second laser pulse then triggers and reads out the fluorescence signal. Improvements should result in a sensitivity of 40 fT/Hz0.5, which would allow detection of proton spins within a second in a microscopic volume. Ref: Thomas Wolf et al., arXiv:1411.6553 [quant-ph] (2014).