Open-path geometry could lead to compact, simple cavity ring-down spectroscopy
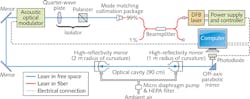
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) takes advantage of the many round trips of light in a high-finesse optical cavity to boost the probe light's path length through the gas being probed, producing very high-sensitivity measurements for atmospheric science—for example, of methane in air (methane is a potent greenhouse gas). Most CRDS instruments used for this purpose have flow cells that are closed-path, in which a vacuum pump pulls the air to be tested through a flow cell within the cavity, with a low-flow purge gas near the mirrors to minimize contamination (and filters used to clean the incoming air as well). Often, the air pressure inside the cavity is also made lower than atmospheric pressure to narrow the linewidths. But the alternative, an open-path configuration, has the advantages of greatly reducing instrument size (by 80% or more), cost, and complexity, and improving the instrument's temporal response.
A group at Colorado State University (Fort Collins, CO) has created an open-path near-infrared CRDS methane sensor, modifying a previous experimental CRDS device by removing its flow cell, pump, and nitrogen purge, opening up the cavity and replacing the hardware with only a small filtered-air purge system with positive-pressure enclosures by the mirrors to keep them clean. The mirrors maintained a reflectivity above 0.99996, allowing an operation time of more than 100 hours. The noise-equivalent sensitivity of 6 × 10-10 cm-1HJ Hz-1/2 is within a factor of three of that for closed-path systems. The wider lines at atmospheric pressure could be accurately fit using appropriate spectral filtering. Reference: L. E. McHale et al., Opt. Express (2016); doi:10.1364/OE.24.005523.

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.