Single-mode telluride glass fiber aims for exoplanet-hunting interferometry
One way to detect exoplanets (planets orbiting other stars) is to use nulling interferometry to combine light from several telescopes that all have relative phase shifts. The nulling interferometer is adjusted until the on-axis light from the star undergoes destructive interference, greatly suppressing the light from the star. In contrast, the off-axis light from exoplanets undergoes constructive interference, allowing the planets to be observed relatively unaffected by light from the central star. To enable the possible detection of life on the exoplanets, the telescopes should be able to image at the spectral molecular lines for water (H2O), ozone (O3), and carbon dioxide (CO2), which are at wavelengths of 6, 9, and 15 μm, respectively. Because the light from the various telescopes is brought into the nulling interferometer via optical fiber, suitable infrared fibers with low loss must be fabricated.
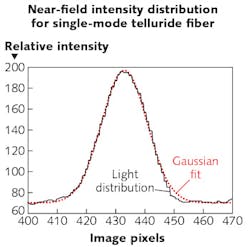
Scientists from the University of Rennes (Rennes, France) and Zhejiang University (Hangzhou, China) have created a new way to fabricate preforms that allows them to make small-core (20 μm), tellurium-germanium-selenium single-mode (at a 10.3 μm wavelength) glass fibers that have a spectral transmission band spanning 3–16 μm and a minimum loss of about 7.9 dB/m. The preform fabrication method shuns the classical rod-in-tube technique. Instead, a capillary method is used in which telluride glass is first formed around a silica fiber and the silica center then etched away with hydrofluoric acid—the resulting capillary is then filled with a higher-index core glass and the fiber drawn. The technique prevents crystallization of the telluride glass. The researchers say it is the first time small-core telluride-glass fibers have been made successfully. Reference: S. Cui et al., Opt. Mater. Express (2016); doi:10.1364/OME.6.000971.
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.
