UCSD lossless metamaterials could make lasers more efficient
University of California San Diego (UCSD) engineers have developed a material that could reduce signal losses in photonic devices. The advance has the potential to boost the efficiency of various light-based technologies including fiber-optic communication systems, lasers, and photovoltaics. The engineers say the discovery addresses one of the biggest challenges in the field of photonics: minimizing loss of optical (light-based) signals in devices known as plasmonic metamaterials.
RELATED ARTICLE: Plasmonic perfect light absorber has a wide IR spectral band
Plasmonic metamaterials are materials engineered at the nanoscale to control light in unusual ways. They can be used to develop exotic devices ranging from invisibility cloaks to quantum computers. But a problem with metamaterials is that they typically contain metals that absorb energy from light and convert it into heat. As a result, part of the optical signal gets wasted, lowering the efficiency.
In a recent study published in Nature Communications, a team of photonics researchers led by electrical engineering professor Shaya Fainman at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering demonstrated a way to make up for these losses by incorporating into the metamaterial something that emits light--a semiconductor.
"We're offsetting the loss introduced by the metal with gain from the semiconductor. This combination theoretically could result in zero net absorption of the signal--a 'lossless' metamaterial," said Joseph Smalley, an electrical engineering postdoctoral scholar in Fainman's group and the first author of the study.
In their experiments, the researchers shined light from an infrared laser onto the metamaterial. They found that depending on which way the light is polarized--which plane or direction (up and down, side to side) all the light waves are set to vibrate--the metamaterial either reflects or emits light.
"This is the first material that behaves simultaneously as a metal and a semiconductor. If light is polarized one way, the metamaterial reflects light like a metal, and when light is polarized the other way, the metamaterial absorbs and emits light of a different 'color' like a semiconductor," Smalley said.
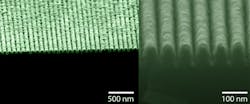
Researchers created the new metamaterial by first growing a crystal of the semiconductor material, called indium gallium arsenide phosphide, on a substrate. They then used high-energy ions from plasma to etch narrow trenches into the semiconductor, creating 40 nm wide rows of semiconductor spaced 40 nm apart. Finally, they filled the trenches with silver to create a pattern of alternating nano-sized stripes of semiconductor and silver.
"This is a unique way to fabricate this kind of metamaterial," Smalley said. Nanostructures with different layers are often made by depositing each layer separately one on top of another, "like a stack of papers on a desk," Smalley explained. But the semiconductor material used in this study (indium gallium arsenide phosphide) can't just be grown on top of any substrate (like silver), otherwise it will have defects. "Rather than creating a stack of alternating layers, we figured out a way to arrange the materials side by side, like folders in a filing cabinet, keeping the semiconductor material defect-free."
As a next step, the team plans to investigate how much this metamaterial and other versions of it could improve photonic applications that currently suffer from signal losses.
SOURCE: UCSD; http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/pressrelease/lossless_metamaterial_could_boost_efficiency_of_lasers_and_other_light_base

Gail Overton | Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.