Simple shearing interferometer measures wavefront of femtosecond laser pulses
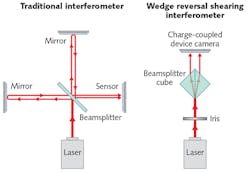
Using an interferometer to characterize the spatial information of a continuous-wave (CW) laser beam can be done straightforwardly using a shearing interferometer, where the test wavefront is interfered with a positionally shifted duplicate of itself. However, measuring ultrafast laser pulses using this method is more difficult because, given the short duration of a femtosecond pulse, traditional interferometers lose their functionality. “A simple interferometer like the shear plate, where the beams reflected from the front and back surfaces interfere, no longer works,” says Chunlei Guo, a professor of optics at the University of Rochester (Rochester, NY).
Now, Guo and his associate, Billy Lam, have come up with a simple shearing-interferometer setup that works well with ultrafast pulses of sub-100-fs duration. In fact, the device, called a wedged reversal shearing interferometer (WRSI), can characterize amplitude, phase, polarization, wavelength, and duration of the pulse. The interferometer contains a single beamsplitter cube with one wedged entrance face, producing an almost zero path-length difference between unsheared and sheared beams, and a very stable interference pattern.
The researchers have used the interferometer to characterize a femtosecond laser beam with a pulse duration of 65 fs. Using a 25 mm beamsplitter cube with a refractive index of 1.5 operating in air, the interferometer can handle a beam diameter of about 8 mm (and needs this diameter to form a sufficient number of usable fringes). Phase-shifting allows the field autocorrelation and the spectrum of ultrashort pulses to be measured and, with the insertion of a linear polarizer, allows the polarization distribution of the beam cross-section to be measured point-by-point. Reference: B. Lam and C. Guo, Light Sci. Appl. (2018); https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-018-0022-0.

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.