Fluorescence imaging system may improve cancer care
Driven to ultimately prevent others from experiencing the pain of losing a loved one to breast cancer, Lumicell (Newton MA) co-founder and chief scientific officer W. David Lee vowed to help improve cancer surgery through more accurate detection of residual cancer in real time following surgical procedures.
“He was searching to find a solution and wanted to work with academics at institutions like Harvard, MIT, and Duke to develop something that could help surgeons better identify residual cancer in breast cancer patients in real time during surgery,” says Daniel K. Harris, vice president of pharmaceutical development and CMC at Lumicell.
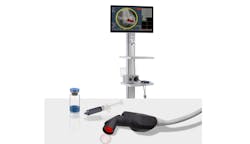
The company, which focuses on fluorescence-guided imaging technologies for cancer surgery, is driving it forward with its LUMISIGHT optical imaging agent. It’s an onco-fluorescent agent administered pre-operatively on the same day as the surgical procedure to highlight cancer cells, as part of the Lumicell direct visualization system (DVS), a fluorescence imaging system used within the lumpectomy cavity (see Fig. 1).
“A probe is used for imaging during surgery,” Harris says. “The imaging drug—the LUMISIGHT optical imaging agent—is administered two to six hours before the procedure, and our probe looks for the signal from that drug.”
The DVS features a red excitation light source out of the front of the probe, while a fluorescence camera filters out that excitation light to generate a fluorescence image. “This is where the drug has been activated and the cancer is,” Harris explains.
The team is also scaling its system for commercial launch in hopes of FDA approval in late 2023.
A supplemental tool
Lumicell’s DVS is an adjunct to the existing standard of cancer care. “We're not coming in and trying to change what they’re doing today,” Harris says. “They’re going in to do the initial lumpectomy as they normally would, and when they believe they’ve removed all of the cancer, they’re going to check their work.” With the probe operating in real time, surgeons can potentially identify cancer missed during the initial procedure and subsequently go back to remove it.
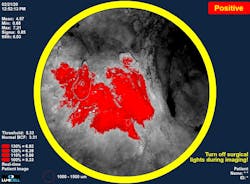
The company has held clinical trials with the system involving more than 700 breast cancer patients at facilities including Massachusetts General Hospital, Stanford, Duke, and the Cleveland Clinic. In these trials, surgeons demonstrated the ability to remove residual cancer left behind during the initial surgery (see Fig. 2).Their agent/probe system addresses a specific challenge in breast cancer surgery: surgeons are challenged to achieve what’s considered a complete cancer resection during the initial lumpectomy.
Approximately 30% of such procedures currently require a second surgery. And 19% of the time, Harris says, cancer is later found in patients who originally were thought to be “clean.” Incomplete tumor resection doubles the risk of recurrence.
Speeding up histopathology
Typically, the gold standard for measuring a surgical outcome is in histopathology, the study of diseased cells and tissues using a microscope. A medical team takes the cancerous tissue specimen that’s been surgically removed and sends it to a lab for analysis. The process involves different stains, and a pathologist determines what’s inside of it.
“This takes a long time,” Harris says, “at least a few days. And typically, reports aren’t available until after the procedure is done. You basically cut out a little bit blindly, and then don’t have a definitive outcome until after the procedure.”
This process is also challenging because pathologists and surgeons can only look at what came out of the patient, not what might still be inside. “We try to study the tissue specimen to see if there is cancer on the outside at the very edge,” Harris says. “And if there is a positive margin, we assume there is probably residual cancer left inside the patient and do a second procedure several weeks later.”
Lumicell’s DVS clears those hurdles.
“We want to transform the way surgeons approach breast cancer surgery and improve outcomes for patients with fewer second surgeries and by removing additional residual cancer that, in some cases, no one ever would have known about,” Harris says. “We want to bring additional information to empower surgeons to take action in real time.”
As they await FDA approval and commercial rollout, the Lumicell team is studying other indications—they believe the drug component of the agent/probe system can be used for all types of solid tumors, including in the brain, prostate, GI tract, and peritoneal metastases.
“We’re looking at expanding this idea to different parts of the body,” Harris says. “We want to transform cancer surgery through imaging.”
About the Author
Justine Murphy
Multimedia Director, Digital Infrastructure
Justine Murphy is the multimedia director for Endeavor Business Media's Digital Infrastructure Group. She is a multiple award-winning writer and editor with more 20 years of experience in newspaper publishing as well as public relations, marketing, and communications. For nearly 10 years, she has covered all facets of the optics and photonics industry as an editor, writer, web news anchor, and podcast host for an internationally reaching magazine publishing company. Her work has earned accolades from the New England Press Association as well as the SIIA/Jesse H. Neal Awards. She received a B.A. from the Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts.