LABEL-FREE IMAGING: Stimulated emission microscopy makes nonfluorescing molecules glow
“It is truly important work,” says Cornell University Professor Chris B. Schaffer of stimulated emission microscopy, described in the October 22 issue of Nature. The approach, pioneered by Wei Min and Sijia Lu and their colleagues under the direction of Harvard University Professor Sunney Xie, exploits the stimulated emission phenomenon, first described by Albert Einstein and the basis for LASER.
This brand new method enables imaging of molecules that absorb, but do not fluoresce at sensitivity levels “orders of magnitude higher than for spontaneous emission or absorption contrast,” explain the researchers. Not only does it enable three-dimensional optical sectioning and allow the use of nonfluorescent reporters for molecular imaging, but according to Xie, “It allows spectroscopic identification of molecules in living organisms and is free from the complication of light scattering by the sample. This opens many new possibilities for biomedical imaging, such as label-free mapping drug distributions and blood vessels in tissues.” Indeed, the Nature paper demonstrates a variety of applications.
Xie explains the approach by pointing out that we experience color primarily because of the mechanism of absorption contrast, whereby the intrinsic energy level of a molecule causes it to absorb specific colors of light–leaving us to see the color of the remaining light. Under an optical microscope, absorption is too weak to measure because each specimen contains just a few molecules. (“The signal is much weaker than those in a conventional UV-vis spectrometer, the sensitivity limit of which is about one part per 10,000 light attenuation,” he notes). Also, light scattering complicates the absorption signal. “For these reasons, fluorescence microscopy has been the dominant contrast mechanism for optical microscopy,” says Xie, who is famous for his work in single-molecule imaging, including the development of coherent anti-Stokes Raman (CARS) microscopy and stimulated Raman spectroscopy (SRS).
The setup
The Harvard team discovered that while non-radiative decay dominates spontaneous emission for chromophores with undetectable fluorescence, stimulated emission can compete–and in fact can become the dominating light decay pathway–when the stimulation field is designed with appropriate energy and timing.
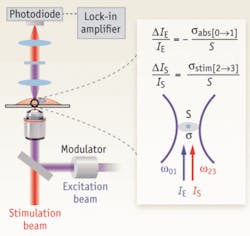
In their system, the incident excitation and delayed stimulation pulse trains are spatially overlapped and focused onto the common focal spot in the sample. A modulator switches the intensity of the excitation beam on and off at 5 MHz. The spectrally filtered stimulation beam is detected by a large area photodiode, and demodulated by a lock-in amplifier to create the image contrast while raster scanning the collinear exciting and stimulating beams (see Fig. 1).
The researchers’ setup consists of two femtosecond (fs) optical parametric oscillators (Coherent/APE) synchronously pumped by a femtosecond mode-locked 76-MHz Ti:sapphire laser (Coherent). Two independent frequency-doubled outputs from these two optical parametric oscillator signal waves, in the wavelength range of 560 to 700nm with pulse widths around 200 fs, serve as either the excitation or stimulation pulse trains. A pulse compressor consisting of a pair of SF11 prisms controls the pulse width. Collinear excitation and stimulation beams are combined and focused with a high numerical aperture (NA51.2) objective onto a common focal spot. The temporal delay between the synchronized excitation and stimulation inter-pulse is adjusted to between 0.2 and 0.3 ps. The intensity of the excitation beam is modulated by an acousto-optical modulator (Crystal Technology) at 5 MHz. A condenser with NA50.9 is used to collect the forward propagating stimulation beam, which is spectrally filtered before being detected by a photodiode. To acquire images with a laser scanning microscope (FV300, Olympus), the team used a 100-ms time constant for a lock-in amplifier (SR844, Stanford Research) and pixel dwell time of 190 ms.
Implications
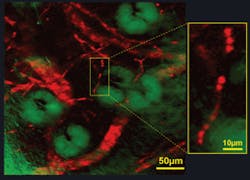
The structure and haemodynamics of blood vessels play a major role in many biomedical processes, such as angiogenesis in tumors and cerebral oxygen delivery in the brain. But established techniques–from MRI, CT, PET, and ultrasound to confocal and two-photon fluorescence microscopy–either lack the spatial resolution needed to resolve individual capillaries or require exogenous contrast agents. Stimulated emission microscopy, however, has proven helpful for such investigations, as demonstrated by the researchers’ ex vivo imaging of the well-developed vascular network from a nude mouse ear.
They excited the Soret band of haemoglobin through efficient two-photon absorption and subsequently stimulated the emission from its Q band, which has a longer excited-state lifetime than the Soret band. The results showed blood vessels branching and looping around sebaceous glands, as well as single red blood cells within individual capillaries (see Fig. 2). While the researchers point out that two-photon absorption has recently been developed to image haemoglobin, they say “stimulated emission is more sensitive because it involves direct one-photon transition. Furthermore, our new technique offers the prospect of three-dimensional mapping of blood oxygenation levels to address a broad range of physiological and pathological problems.”1-3Schaffer, known for his work on blood imaging and nonlinear microscopy, notes that among the molecules visible through this method are many important in biology, “including hemoglobin and cytochrome-c, which play a critical role in oxygen transport and metabolism.” (Xie adds melanin and retinal to that list.) And, Schaffer says stimulated emission microscopy makes it “possible to image these molecules with sub-micrometer resolution inside thick tissues” and with a sensitivity level approaching that of fluorescence methods, “which enable detection of single molecules.”
REFERENCES
- D.M. McDonald and P.L. Choyke, Nature Med. 9, 713–725 (2003).
- A. Grinvald et al., Nature 324, 361–364 (1986).
- D. Kleinfeld, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15741–15746 (1998).

Barbara Gefvert | Editor-in-Chief, BioOptics World (2008-2020)
Barbara G. Gefvert has been a science and technology editor and writer since 1987, and served as editor in chief on multiple publications, including Sensors magazine for nearly a decade.