NEUROLOGY/MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY/AUTISM RESEARCH: High-resolution serial two-photon tomography images whole brains fast
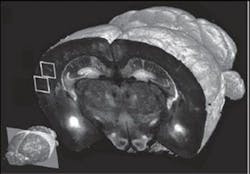
A method of two-photon microscopy is now enabling highly detailed whole-brain imaging. Neuroscientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL; Cold Spring Harbor, NY) and and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT; Boston, MA) developed an approach for automating and standardizing the sectioning and sequential imaging at precise spatial orientations of brain samples. They worked in conjunction with TissueVision (Cambridge, MA) to produce the new technology, called serial two-photon tomography (STP tomography).1 (See the article on "tissue cytometry" for more on whole-organ imaging: www.bioopticsworld.com/articles/2008/07/beyond-cell-cytometry-tissue-cytometry.html). The approach promises to make whole-brain mapping routine, and to facilitate research in mouse models of schizophrenia, autism, and other human brain disorders.
STP tomography makes possible high-throughput fluorescence imaging of whole mouse brains through robotic integration of two fundamental steps: Tissue sectioning and fluorescence imaging. In a paper describing their work, the researchers detail several experiments that highlight the sensitivity and application of the new approach—and they say it is mature enough to be used in whole-brain mapping efforts such as the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas project.
The technology can scan at resolution levels ranging from 1–2 μm to <1 μm; scans at the highest resolution level take about 24 hours, compared to one week using current methods, says associate professor Pavel Osten, who led the work. The team was able to produce full data sets, including final images, in 6.5 to 8.5 hours per brain, depending on the resolution. Each set of 260 coronal (top-to-bottom) slices was assembled by computer into 3-D renderings, which can be broadly manipulated to reveal hidden structures and features. At 10x magnification, the researchers were able to "visualize the distribution and morphology of green-fluorescent protein-labeled neurons, including their dendrites and axons," Osten notes.
The team has already identified susceptibility genes for both schizophrenia and autism, including more than 250 for autism spectrum disorders. Dr. Alea Mills at CSHL has published a mouse model of one genetic aberration in autism, and has many more underway.
1. T. Ragan et al., Nat. Meth., doi:10.1038/nmeth.1854 (2012).
More BioOptics World Current Issue Articles
More BioOptics World Archives Issue Articles