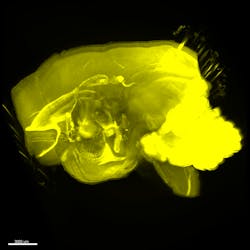
NEUROIMAGING/HIGH-RESOLUTION MICROSCOPY: 'Transparentizing' method enables quick whole-brain imaging at single-cell resolution
Imaging of whole brains at single-cell resolution normally involves not only preparing a highly transparent sample (to minimize light scattering), but also imaging fluorescence-tagged neurons at different slices to produce a 3D representation. Such methods, however, limit the study of how phenomena at the cellular scale correlate with activity at the organism level. Researchers at the RIKEN Quantitative Biology Center (Wako, Japan) have addressed this problem with a new high-throughput method that they call clear, unobstructed brain imaging cocktails and computational analysis (CUBIC).1 It offers unprecedented rapid, high-resolution whole-brain imaging and a simple protocol to clear and "transparentize" the brain sample using aminoalcohols.
The team tested CUBIC, in conjunction with light-sheet fluorescence microscopy, for quick imaging of different size mammalian brains, including mouse and primate, and for capturing spatial-temporal details of gene expression patterns in the hypothalamic circadian rhythm center. By combining images taken from opposite directions, they were able to generate whole-brain images and directly compare brains in different environmental conditions.
CUBIC provides information on previously unattainable 3D gene expression profiles and neural networks at the systems level. Because of its rapid and high-throughput imaging, CUBIC offers opportunity to analyze localized effects of genomic editing. It also is expected to identify neural connections at the whole-brain level.
In the future, explains center director Hiroki Ueda, MD, Ph.D., the research team would like to apply CUBIC to whole-body imaging at single-cell resolution.
1. E. A. Susaki, Cell, 157, 3, 726–739 (2014).

Barbara Gefvert | Editor-in-Chief, BioOptics World (2008-2020)
Barbara G. Gefvert has been a science and technology editor and writer since 1987, and served as editor in chief on multiple publications, including Sensors magazine for nearly a decade.