Microscope uses machine learning to optimize illumination settings
Engineers at Duke University (Durham, NC) have developed a microscope that adapts its lighting angles, colors, and patterns while teaching itself the optimal settings needed to complete a given diagnostic task.
In the engineering team's study, the microscope simultaneously developed a lighting pattern and classification system that allowed it to quickly identify red blood cells infected by the malaria parasite more accurately than trained physicians and other machine learning approaches.
"A standard microscope illuminates a sample with the same amount of light coming from all directions, and that lighting has been optimized for human eyes over hundreds of years," says Roarke Horstmeyer, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Duke University, who is leading the work. However, Horstmeyer explains that computers are able to see things that humans cannot—so he and his team's hardware redesign provides a diverse range of lighting options, which allows the microscope to optimize the illumination for itself.
Rather than diffusing white light from below to evenly illuminate the slide, the engineers developed a bowl-shaped light source with LEDs embedded throughout its surface. This allows samples to be illuminated from different angles up to nearly 90 degrees with different colors, which essentially casts shadows and highlights different features of the sample depending on the pattern of LEDs used.
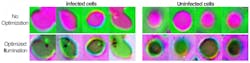
The researchers then fed the microscope hundreds of samples of malaria-infected red blood cells prepared as thin smears, in which the cell bodies remain whole and are ideally spread out in a single layer on a microscope slide. Using a type of machine learning algorithm called a convolutional neural network, the microscope learned which features of the sample were most important for diagnosing malaria and how best to highlight those features.The algorithm eventually landed on a ring-shaped LED pattern of different colors coming from relatively high angles. While the resulting images are noisier than a regular microscope image, they highlight the malaria parasite in a bright spot and are correctly classified about 90% of the time. Trained physicians and other machine learning algorithms typically perform with about 75% accuracy.
Horstmeyer sent the LED pattern and sorting algorithm to another collaborator's lab across the world to see if the results were translatable to different microscope setups. The other laboratory showed similar successes.
"Physicians have to look through a thousand cells to find a single malaria parasite," says Horstmeyer. "And because they have to zoom in so closely, they can only look at maybe a dozen at a time, and so reading a slide takes about 10 minutes. If they only had to look at a handful of cells that our microscope has already picked out in a matter of seconds, it would greatly speed up the process."
The researchers also showed that the microscope works well with thick blood smear preparations, in which the red blood cells form a highly nonuniform background and may be broken apart. For this preparation, the machine learning algorithm was successful 99% of the time.
According to Horstmeyer, the improved accuracy is expected because the tested thick smears were more heavily stained than the thin smears and exhibited higher contrast. But they also take longer to prepare, and part of the motivation behind the project is to cut down on diagnosis times in low-resource settings where trained physicians are sparse and bottlenecks are the norm.
A group of Duke engineering graduate students has formed a startup company SafineAI to miniaturize the reconfigurable LED microscope concept, which has already earned a $120,000 prize at a local pitch competition. Meanwhile, Horstmeyer is working with a different machine learning algorithm to create a version of the microscope that can adjust its LED pattern to any specific slide it's trying to read.
Full details of the work appear in the journal Biomedical Optics Express.
Source: Duke University Pratt School of Engineering press release