Artificial intelligence improves OCT image analysis of the eye
Researchers at the Queensland University of Technology (QUT; Brisbane, Australia) applied artificial intelligence (AI) deep learning techniques to develop a more accurate and detailed method for analyzing optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the back of the eye to help clinicians better detect and track eye diseases, such as glaucoma and aged-related macular degeneration.
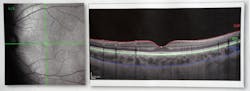
OCT imaging, which is commonly used in optometry and ophthalmology, takes cross-sectional, high-resolution images of the eye, showing the different tissue layers. These images measure around 4 µm. Using OCT scanning to map and monitor the thickness of the tissue layers in the eye can help clinicians to detect eye diseases, says David Alonso-Caneiro, Senior Research Fellow from the Faculty of Health, School of Optometry and Vision Science at QUT, the study's lead author.
"In our study, we looked for a new method of analyzing the images and extracting two main tissue layers at the back of the eye, the retina, and choroid, with special interest in the choroid," Alonso-Caneiro says. The choroid, which is located between the retina and the sclera, contains the major blood vessels that provide nutrients and oxygen to the eye, he explains.
Alonso-Caneiro adds that standard imaging processing techniques used with OCT define and analyze the retinal tissue layers well, but very few clinical OCT instruments have software that analyzes choroidal tissue. Recognizing this, the research team "...trained a deep learning network to learn the key features of the images and to accurately and automatically define the boundaries of the choroid and the retina," he explains.
The team collected OCT chorio-retinal eye scans from an 18-month longitudinal study of 101 children with good vision and healthy eyes, and used these images to train the program to detect patterns and define the choroid boundaries. They then compared what they developed with standard image analysis methods and found their program to be reliable and more accurate."Being able to analyze OCT images has improved our understanding of eye tissue changes associated with normal eye development, aging, refractive errors, and eye disease," Alonso-Caneiro says, as the methods "...could provide a way to better map and monitor changes in choroid tissue, and potentially diagnose eye diseases earlier."
Alonso-Caneiro says the new program had been shared with eye researchers in Australia and overseas, and it was hoped that makers of commercial OCT instruments may be interested in applying it. The team also wants to do further research to test the program on images from older populations and people with diagnosed disease.
Full details of the work appear in the journal Scientific Reports.
Got biophotonics-related news to share with us? Contact Lee Dubay, Associate Editor, BioOptics World
Get even more news like this delivered right to your inbox