LABEL-FREE IMAGING/CARBON NANOTUBES: Transient absorption enables bioimaging of carbon nanotubes
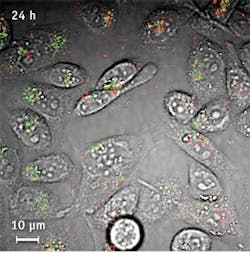
A new, label-free imaging tool that tracks single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) in both living cells and the bloodstream could help to boost the use of the nanotechnology in biomedical research and clinical applications. Until now, no technique has allowed visualization of both metallic and semiconducting nanotubes in these conditions, according to Ji-Xin Cheng, associate professor of biomedical engineering and chemistry at Purdue University (West Lafayette, IN). The Purdue-designed imaging technique, called transient absorption, uses a pulsing near-infrared (NIR) laser to deposit energy into the nanotubes, which then are probed by a second NIR laser.1
A challenge in using transient absorption imaging for living cells is elimination of interference caused by the background glow of red blood cells—which is brighter than the nanotubes. The team solved this problem by separating signals from the red blood cells and the nanotubes into separate “channels.” Light from the red blood cells is slightly delayed compared to light emitted by the nanotubes. The two types of signals are “phase-separated” by restricting them to distinct channels based on this delay. The researchers used the technique to see nanotubes circulating in the blood vessels of mice earlobes in real time. Knowing how long nanotubes remain following injection into blood vessels is important for drug delivery.
SWNT are formed by rolling up one-atom-thick layers of graphite called graphene. The nanotubes are inherently hydrophobic, so some of the nanotubes used in the study were coated with DNA to make them water-soluble, which is required for them to be transported in the bloodstream and into cells. The researchers also have taken images of nanotubes in the liver and other organs to study their distribution in mice. Measuring just ~1 nm in diameter, carbon nanotubes are too small to be seen with a conventional light microscope.
1. L. Tong et al., Nat. Nanotechnol., doi:10.1038/nnano.2011.210 (2011).
More BioOptics World Current Issue Articles
More BioOptics World Archives Issue Articles