PHOTOACOUSTICS/BREAST CANCER: Photoacoustic mammoscopy aims for safer, earlier breast cancer screening
The photoacoustic mammoscope represents an entirely new way of imaging the breast, and hopes to detect cancer earlier than current methods. Instead of potentially hazardous x-rays, which are used in traditional mammography, the photoacoustic mammoscope, designed by researchers in the University of Twente (The Netherlands) Biomedical Photonic Imaging group, uses a combination of benign infrared (IR) light and ultrasound to create a 3D map.
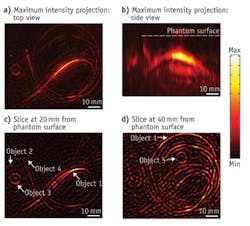
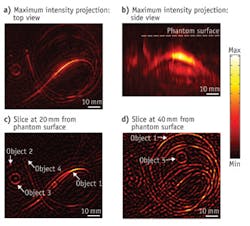
The technique delivers to tissue IR light in billionth-of-a-second pulses. Relatively high absorption by blood increases the temperature of blood vessels, which expand slightly but quickly. While imperceptible to the patient, this expansion generates detectable ultrasound waves that enable formation of a 3D map of breast vasculature. Since cancer tumors have more blood vessels than the surrounding tissue, they are distinguishable in this image.
A small clinical trial showed in 2012 that an earlier version of the technology could successfully image breast cancer in women. In future versions, the researchers expect to improve resolution and add the capability to image using several different wavelengths simultaneously, which promises to improve its ability to detect cancer.
A commercial instrument using this technology would likely cost much less than MRI and x-ray instruments, and would be more in line with ultrasound systems, said Wenfeng Xia, first author on a paper describing the system.1 The next step is to prepare for larger clinical trials; the final prototype will be ready for testing in 2014.
1. W. Xia et al., Biomed. Opt. Exp., 4, 11, 2555–2569 (2013).