Researchers pinpoint role for CD169+ macrophages via 3D/4D image visualization and analysis
To further understand of the causes of cancer as well as the treatment and prevention of infectious and autoimmune diseases, Dr. Patricia Barral of Cancer Research UK (London) and her colleagues are studying the cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling lymphocyte activation and eventual fate.1 Barral's team at the Lymphocyte Interaction Laboratory at Cancer Research UK was the first to establish a role for a group of macrophages in acquiring antigen and presenting intact antigen to follicular B cells in lymph nodesin-vivo. Now, they have identified a novel role for CD169+ macrophages in activating invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells.
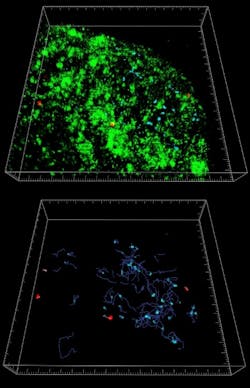
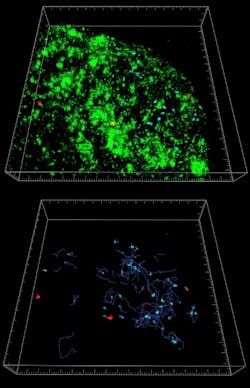
Using 3D/4D image visualization and analysis software (Bitplane's Imaris), Barral and colleagues transformed image stacks acquired from multiphoton examination of the lymph nodes into volume-rendered 4D movies for analysis. Cell movement was automatically tracked and the software also calculated average and instantaneous cell speeds together with displacement and the confinement index. The software was also able to demonstrate the confinement of the iNKT cells in the vicinity of the CD169+ macrophages following administration of particulate lipid antigen by reconstructing the lymph nodes in three dimensions.
In these studies, the team successfully used the software to visualize the long-standing interactions between CD169+ macrophages and iNKT cells, and found fast iNKT activation and cytokine secretion. These processes could be important factors during the early stages of immune responses and host defense.
REFERENCE
1. P. Barral et al., Nature J. of Immunology 11 (4): 303-312 (2010)
Source: Andor Technology
-----
Posted by Lee Mather
Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn
Follow OptoIQ on your iPhone; download the free app here.
Subscribe now to BioOptics World magazine; it's free!