NASA is readying its latest test of laser communications from space to the ground. The Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) built at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Pasadena, CA) arrived earlier this month at NASA's Kennedy Space Center (Cape Canaveral, FL) for delivery to the International Space Station later this year. After being mounted on station exterior, it will be used in 90 days of tests transmitting at 30 and 50 Mbit/s to a one-meter telescope at JPL's Optical Communications Telescope Laboratory on Table Mountain in Wrightwood, CA, in the mountains northeast of Los Angeles.
The main attraction of a laser link from space remains the same one NASA and other developers have cited since the 1960s—the highly directional laser beam can deliver more energy to a receiving antenna than a microwave transmitter. NASA wants the extra downlink bandwidth to deliver high-definition video from the station and high-speed data from space-based scientific instruments. The immediate goal is to downlink 10 seconds of DVD-quality video, with the long-term goal of developing operational optical links, says Michael Kokorowski, OPALS project manager at JPL.
The big challenge is keeping the narrow laser beam tightly directed at the receiver, a problem that long delayed deployment of laser links in space. Intersatellite links were first demonstrated in 2002, but plans for a laser communication link from Mars were scrapped in 2005. In August 2013, NASA will launch the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration on board the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer to demonstrate laser transmission from lunar orbit.Ironically, the problem becomes more difficult at shorter distances between the station and the ground, because the station moves quickly above the surface. That means the 2 W, 1.55 µm fiber laser system on the station must locate and lock onto an optical beacon from the ground receiver. The ground receiver telescope and the gimbal-mounted optical transceiver on the station must move simultaneously, tracking each other as the station passes overhead.
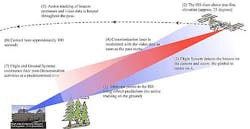
At best, downlinking lasts for only 100 seconds. As shown in the figure, the ground telescope uses orbital data to watch where the station will come into view about 25 degrees above the horizon. The flight system detects the uplink beacon and aims the downlink at the telescope. Once a lock is established, the downlink begins transmitting video data at the ground telescope until the station's orbit takes it below tree level.

Jeff Hecht | Contributing Editor
Jeff Hecht is a regular contributing editor to Laser Focus World and has been covering the laser industry for 35 years. A prolific book author, Jeff's published works include “Understanding Fiber Optics,” “Understanding Lasers,” “The Laser Guidebook,” and “Beam Weapons: The Next Arms Race.” He also has written books on the histories of lasers and fiber optics, including “City of Light: The Story of Fiber Optics,” and “Beam: The Race to Make the Laser.” Find out more at jeffhecht.com.