CMOS camera analysis could help prevent construction industry injuries
Fall arrest systems used in the construction industry come in a variety of designs and are subject to rigorous performance testing. To investigate the effectiveness of different system designs, the Professional Association Institute for Occupational Safety (Berufsgenossenschaftliches Institut für Arbeitssicherheit; Sankt Augustin, Germany) recently conducted a study using anthropomorphic dummies that revealed potential failings in several safety harnesses during a simulated fall arrest. These dangers concerned mainly shoulder straps slipping, along with sternal and dorsal attachments causing injury. The behavior of the harnesses during fall arrest depends significantly on their construction, especially on the arrangement of straps and attachment buckles.
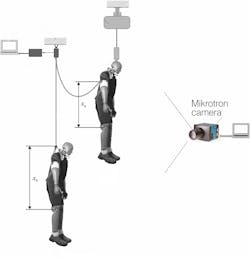
Falls of the anthropomorphic dummy and the behavior of the harnesses during fall arrest were recorded using a Mikrotron (Unterschleissheim, Germany) Cube 7 MotionBLITZ EoSens camera set to 1024 × 1024 pixel resolution at 1410 fps. Its Dynamic Range Adjustment feature allowed the researchers to dynamically adjust the camera’s CMOS sensor for higher contrast scenes. Recorded material was then analyzed using TemaMotion Starter II image identification technology to determine the motion, speed, and acceleration of selected points in sequences of frames.Analysis of fall arrest recordings revealed instances of the sternal attachment impacting the dummy’s face. Pressure was exerted on the dummy’s neck and head as a result of the dorsal D-ring sliding upward along the shoulder straps. In some models of harnesses, the steel buckle traveled along the shoulder straps causing the straps to tighten around the dummy’s neck and head, and potentially injuring the face area.
The majority of safety harness tests are conducted following the methods stipulated in international safety standards calling for the use of a rigid torso dummy, instead of an anthropomorphic dummy which more closely simulates human response. The researchers at Berufsgenossenschaftliches Institut für Arbeitssicherheit believe that the rigid torso dummy is insufficient for a comprehensive evaluation of harness performance and their safety parameters. Considering the significance of the results obtained, the researchers expect to continue testing for other dummy positions, such as head down, head inclined sideways, and positions causing rotation, using the Mikrotron camera. The study of such cases will allow the development of better criteria for assessing safety harnesses and improving their overall design.