Beam power meter for x-ray free-electron lasers is compact, durable
A number of large free-electron lasers (FELs) emitting in the extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) and x-ray ranges have come online within the past decade or so, including the Free-Electron Laser in Hamburg, Germany, the SPring-8 Compact SASE Source and the SPring-8 Angstrom Compact Free-Electron Laser (SACLA; both in Hyogo, Japan), and the Linac Coherent Light Source (Menlo Park, CA). Others, including the European x-ray FEL, the SwissFEL, and the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory XFEL, are under development. These powerful light sources share something in common: the need for a beam power measurement system that is not only accurate, but can stand up to peak powers up to the gigawatt range.
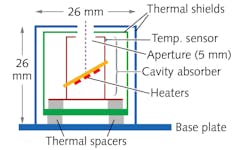
Researchers at the Free-Electron Laser in Hamburg have come up with just such a device-a bolometric radiometer that is only 26 mm on a side, enabling easy measurement of a FEL beam at many locations along the beam. The room-temperature device includes a vacuum-chamber housing and thermal shields—within the chamber is a 1-mm-thick gold plate inside a cylindrical copper shell that has a 5 mm aperture. The absorptance is >99.7% over the 1–60 keV photon energy range. Heaters within the chamber maintain an even temperature of about 300 K to within 40 μK. When a beam strikes the device and the temperature is maintained, the heaters require less current—it is this current that is monitored to determine beam power. Experiments of half a year's time confirmed the bolometer's efficacy and durability. Reference: T. Tanaka et al., Opt. Lett. (2017); https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.42.004776.
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.
