Optical Coherence Tomography/Brain Surgery: OCT-based approach facilitates brain cancer surgery
"As a neurosurgeon, I'm in agony when I'm taking out a tumor. If I take out too little, the cancer could come back; too much, and the patient can be permanently disabled," says Alfredo Quinones-Hinojosa, MD, professor of neurosurgery, neuroscience, and oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "We think optical coherence tomography has strong potential for helping surgeons know exactly where to cut," he adds.
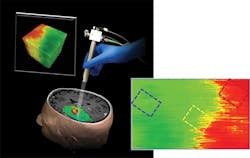
Carmen Kut, an MD/PhD student working in the biomedical engineering lab of Xingde Li, Ph.D., thought OCT might provide a solution to the problem of separating brain cancers from other tissue during surgery. She and her collaborators discovered that brain cancer cells' lack of so-called myelin sheaths had an important effect on OCT readings. So they devised a computer algorithm to process OCT data and generate a color-coded map almost instantaneously. They envision that an OCT scanner would be aimed at the surgical site, and the surgeon could get a continuously updated reading as the surgery progresses.
The team has tested the system on fresh human brain tissue removed during surgeries, and in surgeries to remove brain tumors from mice. The researchers hope to begin clinical trials in patients this summer. If the system eventually goes to market, it will be a big step up from imaging options now available—which are lower-resolution, time-intensive, and/or extremely costly. OCT is comparatively high-resolution, time-efficient, and inexpensive-and unlike competing technologies delivers no ionizing radiation to patients.
The system can potentially be adapted to detect other cancers. Kut is now working to combine OCT with another modality to help surgeons avoid cutting blood vessels.

Barbara Gefvert | Editor-in-Chief, BioOptics World (2008-2020)
Barbara G. Gefvert has been a science and technology editor and writer since 1987, and served as editor in chief on multiple publications, including Sensors magazine for nearly a decade.