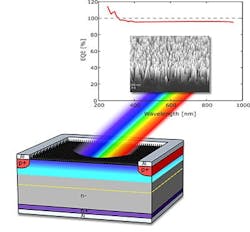
Photodiode has sensitivity above 96% over 250–950 nm wavelength range
A research team at Aalto University (Espoo, Finland) led by Hele Savin has developed a silicon photodetector that can capture more than 96% of the photons over a 250 to 950 nm spectral range. The device doesn't have a conventional p-n junction, but relies instead on an inversion layer formed with a thin-film layer of negatively charged alumina forming a collecting junction in n-type silicon. In addition, the detector surface is nanotextured. The device has a high response for incident angles of up to 70°.
"Present-day light detectors suffer from severe reflection losses, as currently used antireflection coatings are limited to specific wavelengths and a fixed angle of incidence," says Savin. "Our detector captures light without such limitations by taking advantage of a nanostructured surface. Low incident angle is useful especially in scintillating x-ray sensors."
The concept for light detection arose from the team’s earlier research on nanostructured solar cells; indeed, the nanostructure used in the light detector is similar to that used by the researchers a couple of years ago in record-high efficiency black silicon solar cells they produced. The team has filed a patent application for the new photodetector. The prototypes are now being tested in imaging applications related to medicine and safety. The team is seeking new applications for their invention, especially in the UV and IR spectral ranges.
Source: http://www.aalto.fi/en/current/news/2016-11-14/
REFERENCE:
1. Mikko A. Juntunen et al., Nature Photonics (2016); doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.226
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.