Graphene photodetector has 50 GHz speed and 0.6 to 20 micron spectral range
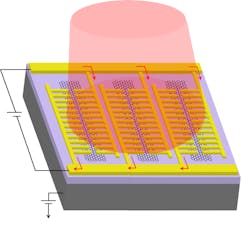
A group at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) has augmented the photodetection capabilities of graphene by forming it into nanostripes connected to patches of gold.1 The device has very broadband sensitivity, from 0.6 A/W at a 0.8 μm wavelength to 11.5 A/W at 20 μm. In addition, the detector is ultrafast, operating at speeds up to 50 GHz.Graphene is an excellent photodetector because it can absorb energy from a broad swath of the electromagnetic spectrum, from the ultraviolet through visible light to the infrared and microwave bands. Graphene is also a very good electrical conductor.
To form the photodetector, the researchers laid strips of graphene over a silicon dioxide layer, which itself covers a base of silicon. Then, they created a series of comblike nanoscale patterns made of gold, with teeth about 100 nm wide.
"We specifically designed the dimensions of the graphene nanostripes and their metal patches such that incoming visible and infrared light is tightly confined inside them," says Semih Cakmakyapan, a UCLA postdoctoral scholar and the lead author of the study. "This design efficiently produces an electrical signal that follows ultrafast and subtle variations in the light's intensity over the entire spectral range, from visible to infrared."
"Our photodetector could extend the scope and potential uses of photodetectors in imaging and sensing systems," says Mona Jarrahi, a professor of electrical and computer engineering, who led the study. "It could dramatically improve thermal imaging in night vision or in medical diagnosis applications where subtle differences in temperatures can give doctors a lot of information on their patients. It could also be used in environmental sensing technologies to more accurately identify the concentration of pollutants."
Source: http://newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/photodetector-improve-night-vision-thermal-sensing-medical-imaging
REFERENCE: 1. Semih Cakmakyapan et al., Light: Science and Applications (2018); https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-018-0020-2

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.