Achromatic Lenses
An achromatic lens, often called an achromat, is a type of optical lens capable of correcting chromatic aberration, a distortion that occurs when glass splits white light into multiple color wavelengths in the spectrum.
Chromatic aberration is a common type of imaging defect. When white light passes through a singlet lens, the wavelengths of light are refracted. Because different wavelengths pass through the glass at different rates, they come into focus at different points on the plane. As a result, the operator will not be able to bring all the colors into focus simultaneously. Chromatic aberration creates blurry fringes of color between dark and light parts of an image, significantly reducing image quality.
To deal with the problem of chromatic aberration, people rely on achromatic lenses, which combine two or more lenses to direct two wavelengths of light, usually red and blue, to the same focal point.
What Makes Achromatic Lenses Important?
Because achromatic lenses bring colors into focus at the same point, they allow users to fully focus an image. Compared to non-corrected singlet lenses, achromats produce much clearer images, which make for easier viewing and a more accurate perception.
When they were first introduced, achromatic lenses brought revolutionary changes to the way we do imaging. Though lenses have continued to improve in quality, the achromatic lens remains a staple in scientific and non-scientific optics applications. Some benefits of achromatic lens assemblies include:
- Improved image quality: By eliminating color fringes, achromatic lenses significantly increase image brightness and clarity. This fact is particularly true for polychromatic imaging.
- Efficient light transmission: Unlike singlet lenses, the on-axis performance of an achromatic lens won’t degrade as aperture size increases, allowing you to utilize the entire clear aperture.
- Cost-effective production: Though improvements on the achromat exist, these lenses are much more expensive. For most purposes, an achromatic lens provides plenty of correction, making it the most cost-effective way to get clear white light images.
Our Advantage
As one of the leading optics manufacturers from China, Shanghai Optics offers a large variety of custom Achromatic lenses for our customers including Achromatic Spherical and Aspherical lenses, Achromatic singlets, doublets and triplets. Combined with one of our advanced AR coatings (covering 400-700nm, 650-1050nm, 1050-2500nm), these optimized lenses are ideal for ensuring high resolution image quality and durability. With our in-house state-of the-art metrology and professional testing personnel, Shanghai Optics is able to provide a full range of inspection reports and CoC( Certificate of Conformance) for full optical characterization such as surface quality, dimensions, centricity, coating transmittance/reflectance (with SHIMADU UV3600 spectrophotometer), and overall/partial surface accuracy (with 6 inches of ZYGO interferometer). FAI inspection reports are available upon request.
Factory Standard
- Shape: Singlet, Doublets or Triplets
- Diameter Tolerance: ± 0.03mm
- Thickness Tolerance: ± 0.03mm
- Radius:± 0.3%
- Focal Length Tolerance: ± 0.5%
- Surface Quality: 20-10 Scratch-Dig(After Coating)
- Surface Flatness: λ/5 @633 nm
- Centration: < 3 arc minutes
- Clear Aperture: > 90% of central dimension
Contact us for manufacturing limit or custom specifications.
Material:
Optical glass, UV fused silica (JGS1), infrared fused silica (JGS3) and calcium fluoride (CaF2), barium fluoride (BaF2) and other crystalline material
How Achromatic Lenses Are Produced
To produce the desired color-correcting effect, achromatic lens manufacturers must use two or more types of optical glass with different amounts of wave dispersion. Typically, this process involves a concave lens element with high dispersion and a convex lens element with low dispersion. The two lenses are attached so that the distortion of one lens closely counteracts the distortion of the other. This type of achromat, called an achromatic doublet, is the most common, though triplet lenses exist as well.
Global achromatic doublet manufacturers like Shanghai Optics use the following basic steps to produce achromatic lenses to meet custom specifications:
- Form the component lenses: Depending on the wavelengths to be corrected, the manufacturer will use different types of optical glass. The mixtures are melted, stirred and then poured into the appropriate spherical optics molds.
- Attach the lenses to form the achromat: The individual lenses are aligned and cemented together so that they’re capable of correcting chromatic aberration effectively.
- Place in the lens assembly: In the manufacturing of an achromatic lens assembly, the achromat is installed along with any other components. Assemblies that incorporate achromats include microscope objectives and telescopes.
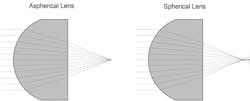
The specific design of the lens will depend on the type of correction required by the application. In some cases, manufacturers may also include aspheric properties to reduce spherical aberration in addition to chromatic aberration.
S.O. follows ISO 9001 standards and uses state-of-the-art metrology equipment to ensure that each achromatic lens performs well and meets our clients’ specifications.