Mirror or Lens: A Simple Guide to the Technical Differences
The disparity between mirrors and lenses lies in the manner in which light behaves upon interacting with their surfaces. When light encounters any surface, it undergoes two primary phenomena: reflection and refraction. The fundamental contrast between mirrors and lenses lies in the fact that mirrors form images through reflection, where light falls onto a mirror, while lenses form images through refraction.
Mirrors: A Reflective Perspective
A mirror, mechanically defined, is a sheet of substrate or metal that reflects incident light. The polished side of a mirror, often coated with a layer of metal amalgam or crafted from naturally reflective metals, facilitates clear reflections of objects placed in front of it.
Mirrors serve numerous practical applications in everyday life, ranging from personal grooming mirrors to more specialized uses such as solar cookers, security applications, periscopes, torch lights, home décor, and telescopes. Various types of mirrors, including plane mirrors, spherical mirrors (concave and convex), each with distinct characteristics, find applications in diverse fields.
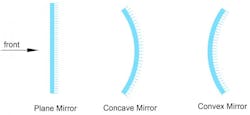
- Plane Mirror: Flat reflective surface producing erect and virtual images.
- Spherical Mirror: Curved reflective surface, divided into concave (inward-facing) and convex (outward-facing) mirrors.
Uses of Mirrors Include:
- Solar Cookers: Utilizing mirrors to focus sunlight for cooking.
- Security and Law Enforcement: Employing one-way mirrors in applications such as surveillance.
- Periscopes: Utilizing mirrors for observation purposes.
- Torch Lights: Intensifying light emitted by torchlights and flashlights.
- Telescopes: Magnifying images by concentrating reflected light.
Lenses: Bending Light for Vision
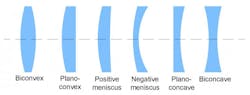
A lens, typically made of glass or transparent material, refracts light that passes through it. Lenses possess two curved surfaces, and the bending of light through these surfaces causes images to appear smaller or larger. Similar to mirrors, lenses can be classified based on their curvature, with convex and concave lenses being the primary types.
Uses of Lenses Include:
- Telescopes and Microscopes: Magnifying objects for observation.
- Spectacles and Contact Lenses: Custom-made to improve vision.
- Torchlights and Flashlights: Concentrating or scattering light beams.
- Projectors: Focusing light to project images.
Types of Lenses:
- Convex Lens: Outward-curving surface causing light beams to converge.
- Concave Lens: Inward-curving surface causing light beams to diverge.
Major Differences Between a Mirror and a Lens:
Mirrors reflect light with a coating on one side, while lenses manipulate light. Lenses are classified into types like simple and compound, with concave and convex variations base d on refraction.
In conclusion, the core distinctions between mirrors and lenses stem from their construction and operational principles. Mirrors reflect light on a single surface, while lenses manipulate light through refraction on two surfaces. Both devices, despite their differences, contribute to a variety of applications and find relevance in numerous fields.
At Shanghai Optics, our expertise lies in providing top-quality custom mirrors or lenses. Explore our range of custom mirror and lens solutions and place your order today. For any inquiries, please feel free to contact us, and we’ll be delighted to assist you.