Exploring Metallic Mirror Coatings
Exploring Metallic Mirror Coatings
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of metallic mirror coatings, focusing on Anti-Reflective (AR) coatings and metal film coatings. These coatings play a crucial role in enhancing the reflective properties of substrates like glass or plastic, effectively turning them into functional mirrors.
AR Coatings
AR coatings, thin films applied to optical materials, aim to reduce light reflection, thereby improving transmittance and visibility. By leveraging the interference effect of light through layered thin films, AR coatings minimize reflections, enhancing the clarity of transparent materials.
AR coatings find application in various products such as eyeglasses, camera lenses, LCD displays, solar panels, and lighting fixtures, mitigating unpleasant reflections and ensuring clear vision.
Metal Film Coating for Mirrors
Metal film coating for mirrors involves applying a thin metal film onto a substrate, significantly enhancing its reflective properties to function as a mirror.
Utilizing electronic vibrations, the metallic film absorbs and reflects specific wavelengths of light, thus improving the reflective capabilities of the substrate. By selectively reflecting light, the metallic layer creates mirrors with superior reflective properties.
Metal film coatings are widely used in household and commercial mirrors, car rearview mirrors, telescopes, and optical instruments. The ability to adjust the thickness and composition of the metallic film allows for customization of mirrors with high reflective properties in specific wavelength bands.
Understanding Front and Rear Mirrors
Front and rear mirrors serve distinct roles in optical equipment and automotive applications, each with unique characteristics and functionalities.
Front Mirror
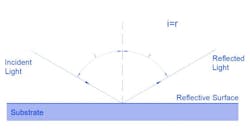
- Position of Reflection: Light reflects off the surface of the mirror. The presence of protective or anti-reflective coatings is crucial as light reflects directly from the mirror’s surface.
- Visibility: Front mirrors offer a direct image, utilizing direct light reflection to produce the field of view.
- Coating: Front mirrors are typically coated with anti-reflective or protective coatings, reducing reflection and minimizing scratches to enhance vision quality.
Rear Mirror
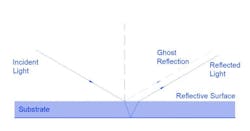
- Position of Reflection: Light reflects on the backside of the mirror. Rear-view mirrors, commonly used in automobiles, enable visibility of the rear of the vehicle while driving.
- Visibility: Rear mirrors employ wide-angle lenses or curved mirrors to provide a broader field of view, offering enhanced visibility of traffic conditions behind the vehicle.
- Coating: Rear mirrors predominantly feature a metallic film coating, providing high reflective properties and ensuring a bright field of view.
Front and rear mirrors fulfill distinct purposes due to their differences in reflective positions, visibility mechanisms, and coatings. Understanding these disparities is crucial for their appropriate application in various contexts.
Types of Metallic Coatings and Their Applications
Various metals are employed in coatings, each with distinct properties and applications:
- Copper: High reflectivity but prone to oxidation, used for shielding high-frequency electromagnetic waves and communication applications.
- Silver: Highly reflective, susceptible to oxidation, commonly used in mirrors, optical instruments, and rearview mirrors.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and reflective, suitable for surface mirrors, optical lenses, and projector reflectors.
- Germanium (Ge): High transmission in the near-infrared, ideal for infrared optical devices like thermography and spectroscopy.
- Magnesium Fluoride (MgF2): Highly transparent with effective antireflection properties, applied to lenses and optical instruments.
- Gold: High reflectivity and conductivity, used in high-end jewelry, decorative optical instruments, and biomedical applications.
- Chromium: Highly reflective and durable, employed in optical filters, mirrors, and spectrometers.
Metallic mirror coatings, including AR coatings and metal film coatings, are essential in various industries for improving visibility, enhancing reflective properties, and enabling precise optical applications. Understanding the characteristics and applications of different metallic coatings facilitates their effective utilization in diverse fields.
Do not hesitate to contact Shanghai Optics today. We’d be more than happy to discuss your projects and how best they can become a success.