Deep Dive into Optics: Surface Accuracy
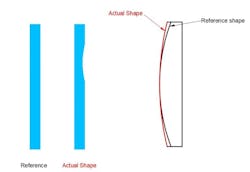
Surface accuracy is the measurement of the deviation between the actual shape and the intended shape of an optical surface.
Surface Accuracy: reference vs. actual shape comparison
Surface accuracy is an important specification of an optical component. Surface accuracy usually is described in terms of fringes or waves that correspond to the interferometer laser wavelength, which is typically 632.8 nanometers for many modern interferometers.
Measuring Optical Surface Accuracy
Test PlateTest plates are used to test window surface flatness, spherical surface power, irregularity, and radius of curvature in optical shops. Prior to interferometers, test plates were the only testing method to verify the flatness of an optical surface by placing a transparent plate (test plate) against a polished surface under test. When monochromatic light shines upon the two contacted surfaces, interference fringes will be observed. Accuracy of optical surface under test can be determined by counting the number of fringes and examining the irregularity of these fringe.
Laser InterferometerLaser interferometers with advanced algorithm software can be used to make precise measurements for optical surface accuracy. A laser interferometer utilizes the effect
Zygo 6″ Verifire XP Interferometer
of interference of light by dividing a beam of light into two beams that travel unequal paths and interfere with each other when reunited. The light interference creates a pattern of light and dark bands called interference fringes. Information derived from the measurement of these fringes is used to determine the power error and irregularity of the optical surface under test.
Screenshot from Zygo Interferometer Test
Laser Interferometer with Computer Generated Hologram (CGH)A CGH (Computer Generated Hologram) acts as a null lens which is inserted into the test arm of an interferometer to test complex surfaces including aspheric and freeform shapes. CGH is calculated to produce a test wavefront matching the nominal shape of the test surface. CGHs in combination with a laser interferometer are commonly used to control the surface accuracy of aspheric lenses during polishing process.
Typical CGH Test Configuration
Contact ProfilometerA contact profilometer is a device which directly measures the surface sag of an optical part with spherical or aspheric shape. The sag values of the test surface is captured and compared with the nominal surface shape as the mechanical stylus travels across the element. Contact Profilometry is the most common and low-cost method for measuring an aspheric surface accuracy by performing a trace across the vertex of the optical part.
Coordinate Measuring InstrumentCoordinate measuring instruments can be directly used to measure the topography of optical surfaces including aspheric and freeform shapes. The basic principle is a point-line-plane reconstruction process: generally, the discrete points on the part surface are scanned and detected by high-precision displacement sensors for obtaining the coordinates of each point, and then the surface shapes are reconstructed. By using advanced data analyze software, the surface accuracy is determined by comparing the surface test data with the nominal surface shape.