Fiber amplifier for telecommunications is based on PbS/CdS QDs
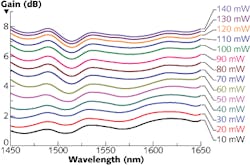
Lead sulfide/cadmium sulfide (PbS/CdS) quantum dots (QDs) that absorb 980 nm pump light and emit in the 1400–1600 nm region are at the heart of an optical fiber amplifier developed by researchers at Shanghai University (Shanghai, China) and the University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ). For use at the standard 1550 nm telecommunications wavelength, the amplifier shows a gain as high as 8 dB in the 1450–1650 nm region as well as better thermal stability than optical amplifiers based on PbS QDs.
Quantum dots with a 6.5 nm core and 1 nm shell were synthesized in organic solvents. To enable the resulting hydrophobic QDs to be dispersed into a polar solvent, the QDs were modified by coating them with amphiphilic copolymers, then combining them with polymers that made the QDs water-soluble. The QD solution was combined with a silicon dioxide (SiO2) sol-gel solution, treated with ultrasound, then deposited onto the tapered region of a fiber coupler to enable efficient coupling of light into a singlemode fiber (SMF). The resulting QD-doped device had a gain at 1550 nm that increased from 1.3 dB for a 10 mW pump power to 8 dB for a 120 mW pump power. The PbS/CdS core-shell QD amplifier had both higher amplification and better thermal stability than amplifiers based on PbS core-only QDs. Contact Xiaolan Sun at [email protected].

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.