Functional near-infrared spectroscopy method could improve neuroimaging
An international team of researchers from the University of Birmingham's School of Computer Science (Birmingham, England) and the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis (St. Louis, MO) has demonstrated critical improvements to functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS)-based optical imaging in the brain. The imaging technology is noninvasive and relatively inexpensive for use in neuroimaging when applied in areas such as functional brain mapping, psychology studies, intensive-care unit patient monitoring, mental disease monitoring, and early dementia diagnosis.
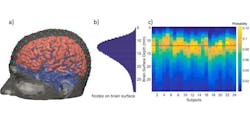
Applying amplitude modulated light known as frequency domain (FD)—rather than the usual continuous-wave (CW) near-IR light—to obtain overlapping measurements of tissue via high-density diffuse optical tomography, the researchers were able to achieve higher resolution in their imaging while also enabling sensitivity to deeper brain regions. FD-NIRS has already been used in such areas as breast-lesion optical tomography, brain-trauma assessment, and joint imaging—here, the researchers compared the FD-NIR application against CW in functional brain imaging.
"I believe this manuscript can be significant from the methods perspective since it addresses important validation about DOT with frequency-domain (FD) data," says Rickson Mesquita of the University of Campesinas' Institute of Physics (São Paolo, Brazil), the associate editor of the journal Neurophotonics, which published the study. "Importantly, their simulations and data appear to show that, by adding the phase information from the FD data, the depth sensitivity is greatly improved. The results are carefully addressed, and the authors' conclusions are of great interest to the fNIRS community."