NASA patents dynamically variable spot size laser system
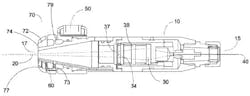
The DVSS lens system is designed so that the optimal brazing distance is in a de-focused area of the lens, which allows for a larger spot size for heating the joining area and accommodates varying sizes of filler metal. That optimal working distance can be in a focused area for zoom lens assembly for welding; in some applications, two separate DVSS laser systems may be used for both brazing and welding applications. In some DVSS system embodiments, the system could be positioned at various angles to provide greater positioning flexibility for joining operations. For example, a mirror may be provided at a 45° angle to position the laser beam at a desired work location; the NASA inventors say a mirror may be positioned at any angle required.Here's the full USPTO filing for those who want to dig more into the technical details of the DVSS.
Industrial Laser Solutions Editors
We edited the content of this article, which was contributed by outside sources, to fit our style and substance requirements. (Editor’s Note: Industrial Laser Solutions has folded as a brand and is now part of Laser Focus World, effective in 2022.)