Rofin upgrades laser doping system for solar selective emitters
Rofin-Baasel says it is readying an upgrade to its PowerLine laser doping systems for crystalline-silicon (c-Si) solar cells, with finer line printings needed for selective emitter processing.
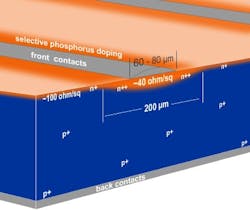
Selective emitters for solar cells promise to add 0.3%-0.5% efficiency to standard homogenous emitters, but with a tradeoff: heavily doping the n-type silicon layer underneath the metallized contact regions achieves low contact resistance and good lateral conductivity, but lightly doping between the contact fingers is necessary to limit recombination and good response to blue light, the company explains.
Original doping widths of 300 μm, designed for around 100 μm wide metallized fingers, were sufficient to account for printer-to-laser alignment. But with process accuracies and fine-line printing now down to 60-80 μm now entering mass production, Rofin-Baasel is upgrading its systems with two new versions of rectangular spot design flat top spot area), of 250 x 500 μm and 200 x 600 μm.
Solar cells with selective emitters. (Source: Rofin-Baasel)
Based on a 80-finger, 156mm c-Si solar cell, reducing the width of the laser doping line under the metallized contact fingers from 300 μm to 200 μm enlarges the total area, with reduced recombination and better blue light response by about 5% and also increases the cell efficiency, the company says.
The system upgrades are available for both new and already installed laser systems; the 300 μm linewidth comes with a new laser resonator version and enhanced beam quality.
Rofin-Baasel's product upgrade announcement coincided with SNEC solar expo in Shanghai earlier this month; it's also a teaser for the company's participation at Intersolar Europe next month (June 13-15) in Munich.