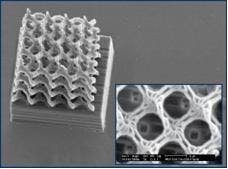
Rankweil, Austria – Two-photon polymerization (2PP) has recently gained interest as an additive manufacturing technology capable of fabricating complex three-dimensional submicron structures using a femtosecond-pulsed near-infrared laser, the “femtoTRAIN™, from High Q Laser Innovation GmbH.
Researchers at the Technical University of Vienna used this method to produce feature resolution down to approximately 100 nm, a level about one order of magnitude better than other methods such as µ-stereolithography. Because of the nonlinear absorption process, it is possible to directly write inside a given volume (a transparent cube, for example) since the polymerization only takes place inside the focus of the laser beam.
Complex 3D structures can be inscribed into a suitable matrix material and/or a resin (such as one that is acrylic based), which is selectively cured. These advantages fulfill the demands for various future applications requiring 3D structures with resolutions in the (sub)micrometer range, such as different mechanical, electronic and optical micro-devices and polymer-based optical waveguides on integrated circuit boards or bio-inspired architectures.
The High Q femtoTRAIN Ti:Sapphire laser offers femtosecond light pulses with a duration of <100 fs at a repetition rate of 73 MHz and an average power of up to 400 mW. It is available at fixed center wavelengths of 790, 800, 810, 850 or 870 nm, respectively. As an option the laser can also be operated at its second harmonic wavelength.
The “femtoTRAIN™ Ti:Sapphire” incorporates the fs-resonator and pump laser in one monolithic housing. Due to the unit's compact size and high stability, it is a good femtosecond laser source for nanostructuring applications like the 2PP method described above.
For more information on the High Q laser, contact: [email protected]