Ultrashort-pulse laser drills 12,000 holes per second with 1 µm diameter
AACHEN, GERMANY – For materials processing, pulsed laser systems with high repetition rates require scanners with speeds up to 1000 m/s, and laser systems with high pulse energy require new beamsplitting and beam-shaping concepts to distribute the energy. One option for making better use of pulse energy is the multibeam concept, which involves splitting a laser beam into many beamlets. At the Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology (Fraunhofer ILT), a team has developed diffractive optical elements (DOEs) for the targeted application of numerous beamlets in micro- and nanostructuring, allowing them to obtain precise results in the submicron range.
The multibeam technique works for periodic structures and requires smooth, flat surfaces—the spacing between holes can be reduced to a few microns. To increase throughput, the Fraunhofer researchers work with a DOE that generates more than 200 beamlets, enabling the drilling of more than 12,000 holes per second, each with an outlet diameter of under 1 µm. The current goal of the researchers is to further increase the drill rate without losing any of the quality. In the near future, drill rates of 20,000 holes per second are possible.
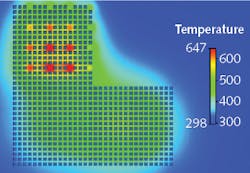
In addition, the researchers have focused on thermal management for multibeam processing by optimizing processes for both single-hole drilling and multibeam processing (FIGURE). In these processes, the laser power deposited must not exceed a maximum value dependent on the material and the target geometry. Using the processes, metallic surface filters with which certain particles can be selectively separated from each other can be economically produced—for example, water filters for multiresistant germs or for microplastics, as well as many other applications in biotechnology.
For more information, please visit http://bit.ly/2WgEF6U.