Lasers are versatile tools used with negligible changeover times in manufacturing processes, but in some areas their uses are still less than optimal, such as in welding. Crack formation and problems with fusion of material can still occur and hinder the quality of construction. The German state of Hesse and Sigma Laser GmbH (Steinbach, Germany) with CEO Shervin Rahimi, in cooperation with Professor Klaus Behler’s team from Germany’s Technical University of Applied Sciences Mittelhessen (THM; Gießen, Germany), researched means to address these issues. They investigated the influence of the temporal modulation of the laser pulses on cracking and geometry of the weld. The results of this research, with high-quality requirements, have implications for a variety of applications, such as in medical technology and aerospace.
Laser deposition welding is a process in which metal is applied on existing components in layers. This technique allows small surfaces to be processed with high resolution when used in conjunction with a well-focused laser beam produced with Super Pulse Technology (SPT). Some manufacturers believe that pulsed radiation can also have a positive influence on the quality of the weld metal’s integrity.
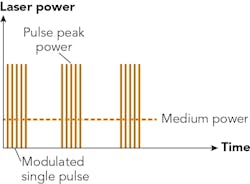
In some instances, depending on the material, geometry, and parameters of the laser pulses, cracks and other welding defects can make the surface rough and thus impair the quality of the workpiece. This is undesirable, especially for medical components. In cases of small melt volumes, there is a risk of overheating in the seam area and damaging the component (FIGURE 1).
The welding material for the research project was supplied in wire form because—in contrast to laser deposition welding with powder—when wire is used, 100% of the coating material goes where it is needed. The process works relatively quickly and causes little distortion. The deposited layer is connected to the substrate conducive to its metallurgy, which results in more durability than can be achieved by other methods of welding. The layer is also dense and provides lasting protection, and the process is environmentally friendly, with no waste.
Wire laser deposition welding also has the advantage of being gravity-independent, making it easier to work on complex surfaces. The smaller surface area of the wire reduces unwanted airborne reactions, thereby facilitating the use of metals such as titanium and aluminum, which are sensitive to those reactions. Titanium and aluminum react with oxygen, nitrogen, and other gases. The smaller the area that comes in contact with oxygen or nitrogen, the less that oxidation can take place. With use of powder materials, however, a large area comes in contact with the gases.
The use of cored wires made of hard materials or high-alloyed metals further expands the possibility of applications. Thanks to the precision of lasers, even complex geometries can be coated. Controllability of the laser allows for high reproducibility and, by extension, efficient production (FIGURE 2). Furthermore, almost all metals can be processed with pulse modulation.When it comes to efficient repair of expensive components or the application of functional layers, laser deposition welding may be essential. It can also be a cost-effective solution, compared to other coating methods.
Solving welding problems
In laser deposition welding, a pulsed laser beam creates a weld pool on the workpiece from the metal of the wire, but high-pulse peak power can quickly overheat this melt and lead to faulty weld seams—tension cracks are often the result. Laser pulse modulation precisely controls the heat input into the material and allows the welding process to be adapted to the solidification characteristics of the materials used (FIGURE 2). Compared with conventional laser welding, the user thereby has control on the nucleation rate during solidification of the metallic melt, producing weld seams with a very fine-grained, homogeneous microstructure (FIGURES 3 and 4). Using two different materials, such as titanium/aluminum and titanium/stainless steel, increases the ductility of the joint and avoids the formation of cracks.Pulsed lasers can play an important role, especially when welding refractory metals such as alloys of tungsten, niobium, zirconium, tantalum, or molybdenum with melting points up to 3500°C. Although these alloys are difficult to process for many types of manufacturing due to characteristics such as extreme corrosion resistance, low thermal expansion, and good conductivity of high-tech heat and power, they are indispensable in the area of high-tech.
Through precise undercooling of the weld pool, thanks to the pulse modulation, a fine-grained microstructure is formed and, by extension, a qualitatively excellent weld seam.
This method also offers advantages in tool and mold making, broadening the range of applications of pulsed laser systems. For example, when processing brittle materials such as castings and carbon steels, the process significantly improves weldability and minimizes reworking costs.
Exploring the possibilities
Thanks to the good focusability of the laser beam, it is possible to process small, complex surfaces with high local resolution, such as medical components, where pulsed radiation improves the surface as well as the metallurgy of the weld metal. The coating material is supplied as a wire with a diameter of less than 0.8 mm. In the German research project, the laser pulses came from a lamp-pumped, pulsed Nd:YAG laser.
A more-efficient solution can be the newly developed SPT control, which regulates the laser pulses in the short-term range and can reduce interruption times to less than 50 μs. This control allows the regulation of pulse durations in milliseconds and time constants in the microsecond range, as well as a modulation of the frequencies up to 3000 Hz.
Stabilizing the welding process
The start pulse of the laser melts the supplied wire and the base material with a relatively short pulse of 1.2 ms duration. The subsequent modulated follow-up pulse of at least 2 ms in length stabilizes the process and controls the duration of the heat input into the melting zone and thus the melt-bath dynamics. In this case, the beam diameter can be adjusted according to the process requirement on the setting of the focus position—for example, by choosing a beam diameter about 0.2 mm larger than the wire diameter used—to sufficiently guarantee the build-up material during build-up welding.
Between the start and stabilization pulses, a longer, temporal interruption of a few milliseconds can also be set. This can ensure, for example, an interim cooling period and thus a limited temperature increase of the melt volume and the heat-affected zone in the base material. The control must be adjusted so that the welding depth is sufficient to achieve a complete connection of weld metal and base material.
In addition, the set pulse rate determines the distance of the seam joint and increasing the modulation frequency makes the joint more uniform, so splattering can be all but completely reduced.
Pulse modulation applications
Based on their findings, the team from Hesse, Sigma Laser, and THM conducted trials on a variety of materials and combinations to coat medical implants or medical devices, combining stainless steel and titanium alloys using pulse modulation techniques. These techniques were well suited for the small dimensions of the components, the correspondingly thin coating, as well as the solidification behavior of the materials requiring low energy input and an adapted heat transfer.
Initial applications show that build-up welding with modulated laser pulses achieves the desired results. It is important to note that in each case the process has to be adjusted with regard to the materials used and their process-related reactions.
The results have aroused the curiosity of those in industries such as aerospace and shipbuilding.
Barbara Stumpp | Freelance Science Writer
Barbara Stumpp is a freelance science writer based in Germany.