Ultralow-threshold polariton nanolaser operates at room temperature
Polariton lasers have extremely low thresholds—a potentially practical feature for ultralow-power compact photonic devices, including quantum optical devices. However, polariton lasers have traditionally required large cryogenic coolers, negating these lasers’ advantages. In addition, there have been difficulties in controlling thermal stability of excitons, especially in nanoscale devices. Now, researchers at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST; Daegu, South Korea), the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, PA), and Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (Gwangju, South Korea) have demonstrated a room-temperature optically pumped polariton nanolaser with potential applications in quantum information systems.
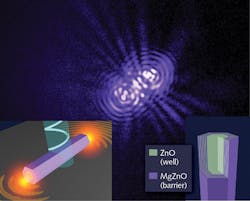
When a material excited by creating Coulomb-bound states of electron-hole pairs (excitons) strongly interacts with photons, a macroscopic quantum state of exciton-polaritons is formed, which receives properties of both the light and the matter, resulting in very energy-efficient polariton lasers. To overcome traditional limitations, the research team created a zinc oxide (ZnO)-based quantum-well structure on the sidewall of a ZnO nanostructure core, which included a zinc magnesium oxide (Zn0.9Mg0.1O) barrier, succeeding in maintaining thermally stable excitons, even at room temperature. The resulting device operates at only one-tenth the power of existing nanolasers and emits at 385 nm.
Chang-Hee Cho of DGIST, who is interested in the lasers from the experimental physics point of view, says, “We are very happy because we can now contribute to building a platform to study physical phenomena related to exciton-polaritons at room temperature.” Reference: J.-W. Kang et al., Sci. Adv. (2019); doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau9338.
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.