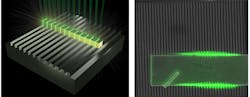
Perovskite laser array has high uniformity and density
Despite rapid improvement in the development of perovskite-based solar cells and micro- and nanolasers, lead-halide perovskite laser arrays are still deficient in wavelength uniformity and packing density. But by paying careful attention to the substrate onto which the nanowire lasers are assembled, researchers at the Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen, China) are now able to fabricate perovskite-based nanolaser arrays with 0.15 nm standard deviation in lasing wavelength and packing density as high as 1250 lasers per millimeter.
Using a solution-processed precipitation method, it was found that nanowires (of a crystalline makeup synthesized with a nominal square shape and atomically flat sides) pumped by a pulsed, frequency-doubled 400-nm-wavelength (1 kHz, 100 fs) femtosecond laser with typical pump density of 6 μJ/cm2 and suspended in air had a much higher quality factor (Q) than nanowires resting on a resist or silicon substrate. By laying these nanowires across a silicon grating with peaks and valleys (an 802 nm period with 460 nm air-gap width), those portions of the nanowire segment that rest on air exhibit extremely uniform lasing properties, as the grating and nanowire geometry can be precisely controlled. Collectively, the nanolaser array can achieve highly uniform lasing wavelength at 540–560 nm wavelengths for applications in biosensing and high-resolution imaging, while being compatible with silicon optoelectronic circuits. Reference: K. Wang et al., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 7, 2549-2555 (Jun. 2016).
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.