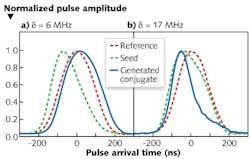
Unlike prior experiments that have used four-wave mixing (4WM) to generate a superluminal pulse (a laser pulse with a group velocity larger than the speed of light in a medium), researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Maryland (both in Gaithersburg, MD) have used a 4WM scheme in a rubidium-vapor cell to generate both a superluminal seed pulse as well as a superluminal conjugate pulse in a different spatial mode (and a different frequency) traveling in a different direction.
In the 4WM process, a 220 mW linearly polarized pump laser is detuned 400 MHz to the blue of the rubidium D1 line. Weak input seed pulses (5 μW peak power) with full-width half-maximum (FWHM) of 200 ns and 5 MHz frequency bandwidth are injected at an angle to the pump and detuned 3 GHz to the blue of the pump beam. As the seed pulse frequency is varied, the relative frequency detuning between the pump and seed beams can be controlled, creating a conjugate pulse that propagates at the same angle as the seed relative to the pump, but in the opposite azimuthal direction. The ability to generate a conjugate pulse that propagates even faster than the superluminally propagating seed pulse by changing the input seed detuning and power could have applications in optical communication schemes in which pulse jitter may be compensated for by advancing or delaying pulses accordingly. Contact Paul Lett at [email protected].

Gail Overton | Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.