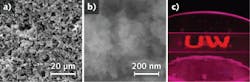
A group at the University of Washington (Seattle, WA) has demonstrated phosphors based on silicon (Si) quantum dots (QDs) that are efficient emitters (with an external quantum efficiency up to 15.9%), can be made to have a peak wavelength that falls anywhere from the near-IR to the green, and can be fabricated cheaply. The phosphors, which are stable at room temperature due to an oxide passivating shell, are nontoxic—unlike otherwise useful conventional QD phosphors based on II-VI semiconductors like cadmium selenide, cadmium zinc selenide, or cadmium zinc sulfide.
Electrochemical etching of a Si wafer produces Si microparticles with attached QDs; these particles are dispersed in ethanol and can be made to react with alkoxysilanes to form a suspension in nonpolar solvents for further processing. The red-emitting version of the phosphor has a broadband excitation band with a 70% excitation efficiency between 345 and 475 nm—a good match for blue- and violet-emitting gallium nitride-based LEDs (the figure shows excitation at 365 nm). The red phosphor in solvent can be formed into thin films by drop-casting or spin-coating. Scanning-electron micrographs of the films show micron- and submicron-sized clusters. Such red phosphors are needed to improve the color rendition of white LEDs. Contact Chang-Ching Tu at [email protected].

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.