Spatial modulation of femtosecond laser writes 3D waveguides in glass
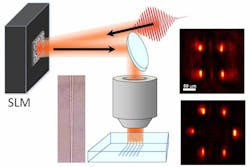
Femtoprint project members are not the only ones using femtosecond lasers to fabricate in-glass microstructures. A team of researchers at the University of Kyoto and the New Glass Forum Research Laboratory (both in Kyoto, Japan) are also using femtosecond lasers—but in conjunction with a spatial light modulator (SLM)—to fabricate 3D waveguide splitters in glass.
In the experimental setup, an 800 nm Coherent (Santa Clara, CA) Mira-Legend femtosecond laser with 120 fs pulse duration and 1 kHz repetition rate was input to an 800 × 600 pixel liquid-crystal-on-silicon SLM and focused into a silica glass substrate. The SLM was programmed with a particular pattern, creating a computer-generated hologram that produced four spatially separated light spots within the substrate. The four light spots produced a 1 × 4 splitter with the four output arms separated in a 3D square pattern from the single input arm. As with the Femtoprint technique, the femtosecond laser induces local refractive-index changes at multiple-beam-spot focused locations within the glass that act as waveguides for input radiation. A 635 nm signal coupled into the splitter via an optical fiber saw an output splitting ratio of 28:23:25:24; work is ongoing with higher-repetition-rate lasers to make more circular waveguides. Contact Masaaki Sakakura at [email protected].