LIGHT-EMITTING DIODES: Microlens arrays improve the extraction efficiency of nitride LEDs
The light-extraction efficiency of quantum-well (QW) light-emitting diodes (LEDs) is one of the keys to the quantum efficiency of these devices. In III-nitride devices, the large refractive-index difference between the gallium nitride and air poses a problem. Numerous attempts to improve light-extraction efficiency of nitride quantum-well LEDs have not been successful in terms of cost, process control, or scalable production. Now, an inexpensive new approach using microlens arrays on top of the quantum-well structure has led to a significant increase in extraction efficiency, and is simple to control and scalable, say researchers at Lehigh University (Bethlehem, PA).1
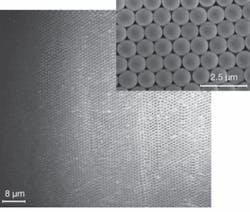
A team of optical and materials engineers led by assistant professor Nelson Tansu created the microlens array directly on top of an indium gallium nitride (InGaN) QW LED device. Uniform microspheres in colloidal suspension tend to spontaneously create a two-dimensional crystal, so the rapid convective deposition of a monolayer of polystyrene (PS) microspheres directly onto the top of LED structure is “practical and straightforward,” according to the researchers. A second layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) was then flowed on top of the PS layer and heated to 140°C. This process melted the PS microspheres, forming a close-packed layer of hexagonal, lenslike arrays (see Fig. 1).
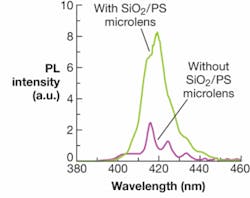
The use of SiO2/polystyrene microlens arrays on the top surface of the LED allows the photons emanating from the QW to scatter away from the structure with a larger effective “photon escape cone,” leading to increased light-extraction efficiency. In addition, the reduced refractive indices of SiO2 (n = 1.46) and polystyrene (n = 1.58) in the microlens arrays leads to reduced Fresnel reflection at the interface of the air, GaN, and microlens array. The photoluminescence (PL) peak intensity of the samples at λpeak = 419.3 nm exhibited a 233.6% improvement with the microlenses than without (see Fig. 2). The integrated photoluminescence for samples covered with the array showed an improvement of 269% over the uncoated sample. And at 480 nm, output is improved by 219% with use of the microlens arrays.At low current levels of 5 mA, the relative external quantum efficiency of the LEDs was improved 4.34 times with the SiO2/PS layer. For 100 mA, the improvement was 3.32 times that of LEDs with no microlens arrays on top.
Further understanding is required, and the Lehigh group will continue to research better light-extraction efficiency of the QW LEDs. “We plan to conduct comprehensive modeling and parametric studies to optimize the sphere diameters and the PS layer thickness, and to optimize the fabrication of the arrays,” says Tansu.
REFERENCES
1. Y. Ee et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 221107 (Nov. 26, 2007).
About the Author
Valerie Coffey-Rosich
Contributing Editor
Valerie Coffey-Rosich is a freelance science and technology writer and editor and a contributing editor for Laser Focus World; she previously served as an Associate Technical Editor (2000-2003) and a Senior Technical Editor (2007-2008) for Laser Focus World.
Valerie holds a BS in physics from the University of Nevada, Reno, and an MA in astronomy from Boston University. She specializes in editing and writing about optics, photonics, astronomy, and physics in academic, reference, and business-to-business publications. In addition to Laser Focus World, her work has appeared online and in print for clients such as the American Institute of Physics, American Heritage Dictionary, BioPhotonics, Encyclopedia Britannica, EuroPhotonics, the Optical Society of America, Photonics Focus, Photonics Spectra, Sky & Telescope, and many others. She is based in Palm Springs, California.