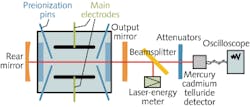
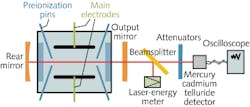
Pulsed electric-discharge DF laser produces 4.95 J pulses
The deuterium fluoride (DF) laser is most well-known in the form of high-powered military chemical lasers such as the US Navy’s Mid-Infrared Advanced Chemical Laser (MIRACL), which could emit up to 2.2 MW of continuous-wave power at 3.8 μm for a minute or so. However, much smaller-scale electrical-discharge DF lasers are possible; if average-power outputs of watts rather than megawatts are acceptable, these pulsed lasers come with advantages such as simplicity, safety, and operation without corrosive gases. So-called “nonchain” (lacking a chemical chain reaction) electrical-discharge DF lasers emit in the 3.6 to 4.2 μm range and have applications that include spectroscopy and laser ranging.
Scientists at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun, China) and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing, China) have modeled the nonchain DF laser and used the results to build a prototype laser with an optimized sulfur hexafluoride-to-deuterium (SF6 to D2) mixture ratio and output-mirror reflectivity of 10:1 and 30%, respectively. The model, which was based on laser rate equations theory, included 28 different reactions simulating chemical dissociation, pumping, de-excitation, and stimulated emission. The prototype comprised main electrodes, preionization pins, a rear mirror, an output mirror, a beamsplitter, a laser-energy meter, attenuators, a mercury cadmium telluride detector, and an oscilloscope. With a pulse duration of 148.8 ns, the prototype produced 4.95 J single pulses with a peak power of 33.27 MW. Contact Jijiang Xie at[email protected].