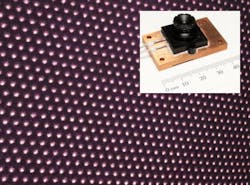
Near-IR structured-light spot projector for machine vision is VCSEL-based
Princeton Optronics (Mercerville, NJ), which makes high-power vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) and VCSEL arrays for illumination and other uses, has unveiled high-peak-power (8 W) 860 and 940 nm laser projectors for 3D-imaging applications in machine vision and robotics.
In the device, the VCSEL array and its associated lens project a large hexagonal array of near-IR spots across whatever target scene the user is interested in; the array of spots serves as structured light that can be captured and analyzed by a separate user-provided machine-vision or robotics stereoscopic camera and associated software to determine the spatial structure, distance, and positions of objects in the scene. Such scenes could be, for example, objects passing by on an assembly line, or a robot's surroundings.
Normally, 860 nm illuminators are used for indoor applications and 940 nm illuminators for outdoor applications where solar background in present. Princeton Optronics says its VCSEL-based projectors produce very high contrast spots, which extends their detection range. The arrays typically have a wavelength bandwidth of +/-5 nm and an efficiency of greater than 40%.
For more information, see www.princetonoptronics.com.
Source: Princeton Optronics
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.