Perovskites now tapped to make much-less-expensive Faraday (polarization) rotators
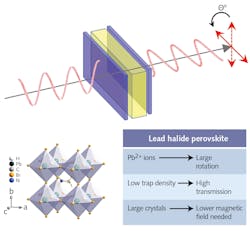
Having proved successful in solar cells and myriad other optoelectronic devices, lead halide perovskite (LHP) materials continue to be explored as low-cost alternatives to many long-established silicon and crystalline semiconductors. In the case of Faraday rotators—optical components that rotate the plane of polarization of forward- and backward-propagating light in the same direction—used in optical isolators and circulators, scientists at the University of Sydney and the University of New South Wales (both in Sydney, Australia), as well as Monash University (Clayton, Australia), have demonstrated the viability of the single-crystal LHP methylammonium lead bromide (MAPbBr3) as a lower-cost alternative to the industry standard terbium gallium garnet (TGG).
Unlike TGG, which is grown using the Czochralski method at high heat (1500ºC) in an inert atmosphere, MAPbBr3 crystals from 1 to 4 mm thick were grown using solution-processed methods and found to have a Verdet constant (a measure of the Faraday effect) of 1X up to 2.5X with lower temperature dependence from 570 to 700 nm compared to TGG. Even though they found higher absorption loss than for TGG, the scientists calculated that an MAPbBr3 optical isolator could still achieve 95% transparency with lower temperature dependence and with 40 dB isolation for input powers up to 2 W. Manufacturing costs for a MAPbBr3 single crystal are expected to be between on to two orders of magnitude lower than for a TGG crystal. Reference: R. P. Sabatini et al., Adv. Sci. (Feb. 13, 2020); https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/advs.201902950.
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.