Dual-wavelength fiber laser uses low-cost double-ring configuration
Although dual-wavelength fiber lasers can be constructed using nonlinear methods or by integrating optical filters such as fiber Bragg gratings, Fabry-Perot filters, or other bandpass filters inside the gain cavity, these techniques are complex and expensive. Instead, researchers at the Industrial Technology Research Institute (Hsinchu, Taiwan), National Chaio Tung University (Hsinchu, Taiwan) and Yuan Ze University (Chungli, Taiwan) have developed a compound-ring architecture that lases at two wavelengths simultaneously and is much lower in cost.
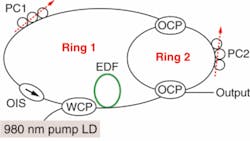
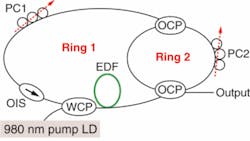
The dual-ring architecture consists of a standard erbium-doped-fiber ring-laser configuration-a 110 mW, 980 nm laser coupled into a 10 m length of erbium-doped fiber and protected by an optical isolator. The second ring is coupled into the first using two 3 dB optical couplers, with each ring having its own polarization controller to adjust the power level of the lasing wavelengths. The laser oscillates at a frequency that satisfies the resonant conditions of the main cavity and the subring cavity, which were designed with specific fiber lengths to produce dual-wavelength lasing at 1560.17 and 1561.93 nm, with output power levels of approximately 8.1 and 7.1 dBm, respectively. Contact Chien Hung Yeh at [email protected].