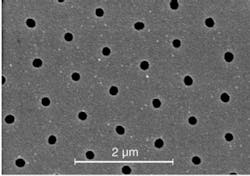
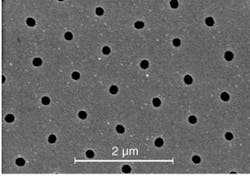
Microspheres simplify nanopatterning processes
Commercially available microspheres are being used in numerous applicationsfrom creating white-light sources by coating red and green fluorescent microspheres on blue light-emitting diodes (see www.laserfocusworld.com/articles/318539), to acting as dyed biomaterials in laser-removable tattoo inks (see www.laserfocusworld.com/articles/255480). Now, researchers at Northwestern University (Evanston, IL) have extended the range of uses for microspheres by applying them in a self-assembling array for maskless nanopatterning. Basically, microspheres of varying size and material composition are flowed in solution and uniformly self-assemble over the substrate to be patterned. This planar array of spheres acts as a set of tiny lenses to focus light onto the substrate and create the desired patterneither nanoholes (for negative photoresist substrates) or nanopillars (for positive photoresist substrates).
Similar work is being performed at Johannes Kepler University (Linz, Austria), but the Northwestern team says it does not use an expensive ultraviolet (UV) laser as the source in a relatively slow rastering mode, but instead can use any broadband UV source in a single-shot, high-throughput exposure to create the desired holes or pillars. Such patterned nanostructures are finding use in solar cells, nanofiltration systems, and fuel cells. Contact Hooman Mohseni at [email protected]