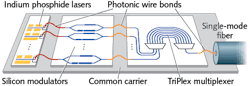
Free-space photonic wire bonds connect III-V and Si photonics on separate chips
Photonic wire bonding is a technique developed at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT; Karlsruhe, Germany) in which photonic waveguides are written with an ultrafast laser into a photoresist material via two-photon lithography, producing free-space photonic “wires” that can optically connect disparate components on a photonic chip, just as electronics can be connected via conventional metal wire bonding. The technique has now been improved by researchers at KIT, Vanguard Photonics (Karlsruhe, Germany), and the Heinrich Hertz Institute (HHI; Berlin, Germany) so that it can reliably connect indium phosphide (InP) III-V laser diode light sources on one chip to silicon (Si) photonic circuits on a separate chip with insertion losses of as low as 0.4 dB. The researchers say that this is the most efficient connection ever made between InP lasers and Si photonic chips (connections are shown in red in the figure).
The photonic wire bonds were fabricated using laser pulses with a 780 nm center wavelength, 100 fs duration, and 80 MHz repetition rate. The material for the wires was a negative-tone photoresist made by Nanoscribe (Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany), an additive manufacturing and lithography company that in itself is known for its photonic-wire-bonding capabilities. The 1/e2 diameter of the writing laser beam was set to be about 3 µm. The InP lasers to be connected to the Si circuit had a horizontal-cavity surface-emitting laser (HCSEL) geometry, and the photonic wire bonds included a rectangular taper to match the HCSEL output area. On the Si-circuit end of the photonics wire bond, a tapered Si nanowire produced via UV lithography was embedded in the polymer end to enhance coupling into the Si photonics. Reference: M. R. Billah et al., arXiv:1802.03454v1 [physics.app-ph] (Feb. 9, 2018).

John Wallace | Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.