Until now, most thin-film organic lasers have relied on distributed-feedback (DFB) resonators fabricated by electron-beam lithography. Now there may be a simpler solution. A German research team has fabricated a mechanically flexible conjugated polymer laser with a two-dimensional (2-D) photonic band structure without relying on standard lithographic techniques. The surface-emitting photonic crystal laser uses an embossed nanopatterned substrate with conjugated ladder-type poly(p-phenylene) polymer (LPPP) as the active layer. With optical pumping of the device, there is nearly diffraction-limited laser emission perpendicular to the substrate, and both the threshold and the differential efficiency improve significantly compared to systems with one-dimensional (1-D) distributed feedback.
Scientists contributing to the organic laser project are from the Lehrstuhl für Photonik und Optoelecktronik, Ludwig-Maximilians Universität (Munich, Germany), the Fraunhofer Institut für Solare Energiesysteme (Freiburg, Germany), and the Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung (Mainz, Germany). According to Ludwig-Maximilians researcher Uli Lemmer, their findings can be explained within a Laue formulation for the feedback mechanism in the photonic crystal. In this process, elastic Bragg scattering can couple two waves that have the same energy level to produce constructive interference that leads to positive feedback and the formation of a laser mode in an optically amplifying medium.
Laser fabrication begins with a mechanically flexible poly(ethylene terephtalate) substrate with an acrylic coating to which a 2-D periodic height modulation is introduced through an ultraviolet embossing process. The device's active layer, approximately 300-nm-thick LPPP, is then spin-coated onto the substrate.
Laser excitation comes from a frequency-doubled regeneratively amplified modelocked Ti:sapphire laser that produces 400-nm, 150-fs pulses. Laser action occurs through feedback within the plane of the waveguide, and the laser radiation is then coupled into radiation modes perpendicular to the substrate through first-order Bragg diffraction.
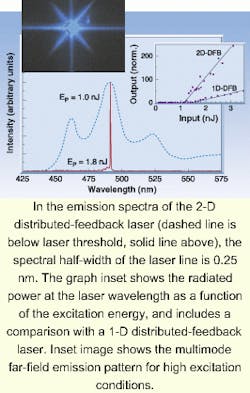
As a result, the researchers were able to identify the participating laser modes using the device's far-field emission pattern (see figure). They recorded emission spectra with a spectrometer and charge-coupled-device (CCD) detector with a spectral resolution near 0.25 nm and recorded the emission pattern with a CCD camera. To measure the beam profile, the sample was revolved on a rotation stage while the emitted intensity was recorded through a 100-µm pinhole placed just a few centimeters away, which produced an angular resolution of 0.35 mrad.
The scientists compared the emission intensity produced to that of a laser with an LPPP film of the same thickness, an equivalent substrate, a purely 1-D periodic height modulation, and the same maximum amplitude. In essence, the laser threshold of the 2-D structure was 30% lower, and its differential efficiency higher. In addition, while a strongly polarized emission with high divergence parallel to the grating lines was observed with 1-D feedback, the 2-D structure developed by the German scientists achieved highly directed nonpolarized emission. After studying the emission pattern's corresponding transverse irradiance profile, the group determined the angular radius of the far-field emission to be 2.4 µrad, which indicates nearly diffraction-limited emission from the entire area of the excited spot.
About the Author
Paula Noaker Powell
Senior Editor, Laser Focus World
Paula Noaker Powell was a senior editor for Laser Focus World.