Gravity, it can be argued, is the force that binds the universe together. It's also a key piece of the theory of general relativity. But, despite its being such a fundamental force, there's no way of measuring it beyond variations on plain old falling down.
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), being built by the California Institute of Technology (Pasadena, CA) and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Cambridge, MA), aims to address that lack by detecting distortions in the shape of space caused by waves of gravity. Similar projects, such as the VIRGO interferometer being built in Italy by French and Italian researchers, have the same goal. To achieve the necessary sensitivity, LIGO and VIRGO must be able to measure very tiny movements—so tiny that even a small temperature change in a mirror could make enough noise to drown out the signal being sought.
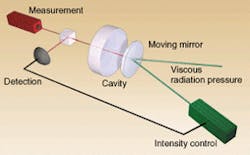
Physicists at the Ecole Normale Supérieure and Université Pierre et Marie Curie (both Paris, France) have been working on a technique for reducing the thermal noise in mirrors for gravitational interferometers. They use a laser to measure perturbations in the mirror and apply another beam to damp out the motion through radiation pressure.
Scheduled for completion next year, with observations to begin in 2002, LIGO consists of two interferometer arms, each 4 km long. One will be in Hanford, WA; the second will be 3030 km away in Livingston, LA. Each contains a freely suspended test mass. Light from a laser source will pass through a beamsplitter and be divided evenly between the two arms. On their return journeys from the arms, the beams will destructively interfere so that a photodetector will see no light in the absence of motion. A gravitational wave will cause a tiny movement in the test masses, knocking the reflected beams out of phase so that the photodetector will see light.
The project will let scientists test general relativity's prediction that gravitational waves exist and that they propagate at the speed of light. It may also provide experimental proof that there really are black holes and measure gravitational ripples caused by two black holes colliding.
In the French experiment, the researchers used a 1.5-mm-thick silica plano-convex mechanical resonator with a diameter of 14 mm and a curvature radius of 100 mm. The mirror was coated on the plane side. A front mirror with a curvature radius of 1 m was placed 1 mm from the rear mirror. A Ti:sapphire laser emitting at 810 nm, with an intensity-stabilized and spatially filtered beam, illuminated the optical cavity. Phase fluctuations of the reflected light were sent to a spectrum analyzer and to a feedback loop. The feedback loop consisted of an amplifier with variable gain and phase driving an acousto-optic modulator. As the beam measured thermal fluctuations in the system, the feedback loop applied varying levels of radiation pressure to the mirror, cooling it (see figure).
The researchers said their technique enabled them to reduce thermal noise in the mirror by a factor of 20. That reduction makes the mirror sensitive to spatial movements on the order of a billionth of an angstrom. With that kind of sensitivity, researchers should be able to measure what Einstein could only imagine.
About the Author
Neil Savage
Associate Editor
Neil Savage was an associate editor for Laser Focus World from 1998 through 2000.