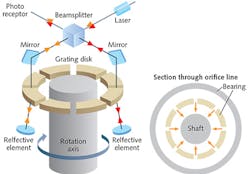
Passive ceramic cooler shields optics within rotary laser scanners
The trends of miniaturization and high-speed performance in today's optoelectronics industry place demands on a product's thermal and optical properties. For example, digital rotary scanners that focus laser light onto a rotary drum to create a reflective full-sized copy of a drawing contain optics at one end of the spinning axis of the scanner. To prevent vibration, the metal shaft at the center of the rotary scanner is cushioned by an air bearing that runs at high speed and can transfer heat to the shaft that in turn can transfer to the optics and negatively affect focusing precision.
Because these rotary scanners have little room for active thermal control and would otherwise require an optical redesign to function with a high heat load, rotary scanner manufacturers have discovered that a MACOR mica glass-ceramic material from Corning (Corning, NY) can be inserted between the rotating shaft and the optics to provide passive thermal and electrical insulation. It can be machined using conventional metalworking tools with no post-firing requirements, and is stable in high-temperature environments (continuous at 800°C up to 1000°C peak) with zero porosity and outgassing. A radiation-resistant, passive thermal and electrical insulator with low thermal conductivity, MACOR can be machined to a surface finish of less than 0.5 μm and polished to a smoothness of 0.013 μm. Contact Franck de Lorgeril at [email protected].
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.